Vertebral column Flashcards
(50 cards)
how many vertebrae in adult vertebral column?

when do sacral verebrae fuse?
late puberty
curvatures of vertebral column?
primary curves (concave anteriorly) = thoracic + sacral/coccygeal (first to form in embryo)
secondary (convex anteriorly) = cervical + lumbarr

when do cuvratures of the vertebral column develop?
how do they develop?
thoacic and sacrococcygeal cuvratures are established in foetal development
cervical and lumbar secondary curves develop in infancy
- 2-3 months = independently hold head, compensatory secondary curvature develops in cervical region
- 6-8 months = further compensatory secondary curvature in lumbar region
1* are caused by the shape of the vertebrae
2* curves arise from changes to shape of intervertebral disc
(degeneration of discs in elderly results in more pronounced primary curvature)
some examples of pathological vertebral curvatures? (3)

black line seperating?

vertebral body (top)
vertebral arch
juvenile vertebrae parts
never call centrum vertebral body - as vertebral body is more than just centrum (+ neural arch)

what is adult vertebral body derived from?
juvenile centrum plus and small portion of the neural (vertebral) arch
explain ossification of the centra (centrum)
where does it first appear?
progression?
begins in mesenchymal stage (undifferentiated mesoderm)
ossification begins dorsal to the notocord
true endochondral ossification (center -> periphery)
first appears in lower thoracic an upper lumbar regions (T10-L1) between 9-10 foetal weeks
bidirectional progression (reaches L5 by 3rd month and C2 by 4th foetal month)
(white is notocord)
(bottom area is centrum)
(black is ossification)

why is there a ring-shaped area of ossification of the centra?
notochord cells contain angiogenic inhibiting factor which delays vascular penetration to this region
so vertebral centra fro first trimester have an avascular region around notochord
this results in ring-shaped ossification
vascular supply centra?
avascular area around notochord
note that developing centrum has lots of grooves due to vascular supply

explain ossification of the neural arches
starts on inner surface of each hemi-arch
intramembranous ossification followed by endochonral

when does ossification of neural arches first occur and where?
progression?
initiation??
first appear in lower cervical and upper thoracic regions in 2nd foetal month
then spreads upwards and downwards
ossification in upper cervical/lower throacic initiated in response to gasp reflex (muscle contraction)
by 3rd foetal month ossification in lower throacic and upper lumbar regions
ossification here is initiated in response to lower limb movement (muscle contraction)
when and where does neural arch fusion occur?
when do cervical arches fuse?
lowest lubar arches?
therefore…..
1st year of life - neural arches fuse posteriorly at the spinous processes (at the posterior synchondrosis)
- occurs initially in lower throacic and upper lumbar regions and progresses upwards and downwards
cervical arches may not fuse until 2nd year
lowest lumbar arches may not fuse until end of the fifth year
therefore in any individual <6 y/o some degree of non-fusion of arches should be expected (not to be mistaken for fracture)
NB: a synchrondrosis is a primary cartilaginous joint (2 bones seperated by hyaline cartilage - hyaline cartilage can turn to bone with advancing age which is exactly what happens here)

neurocentral fusion?
when does it occur?
adult vertebral body formed from?
fusion between neural arches and centra (occurs ventral to pedicles at neurocentral junction)
occurs between 2-5 years
adult vertebral body formed from centrum and “boutons” of pedicles
- head of costal processes (ribs) only every articulates with these boutons and never with the centrum

where does neurocentral fusion occur first?
last?
1st = lumbar region
followed by cervical segment
last = thoracic vertebrae (possibly due to delay caused by ribs)
does neurocentral junction go away?
no it is maintained throughout life
it is an area of fracture weakness
many vertebral fractures occur at area of neurocentral fusion

…
C1 also called?
ossification?
what is different about C1?
incomplete ring?
atlas (top of the world)
C1 ossifies from 3 primary centres
still have neural arches, no centrum (anterior arch/bar instead)
incomplete ring up until about 2 years as anterior arch takes longer to form than neural arches
pic (A = appearance, F=fusion)

neurocentral ossification C1?
shouldn’t really be called this because there is no centrum
but occurs at 5-6 years

when should you expect a complete fused C1?
5-6 years
what will C1 initially appear as at birth?
appearance?
7 weeks?
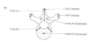
2 neural arches (bony masses)
- larger concave articular facets anteriorly on upper surface
- smaller flatter articular facets on lower surface
at 7 weeks the centre for these lateral masses appears (posterior to articular pillar)
(articular pillar is part that articulates with occipital condyles)
(so its the little wedge shaped area in the first image)

how to differentiate between superior and inferior facets of atlas (C1) at birth?
superior facets are much larger (bear weight of skull, atlanto-occipital joint)
inferior facets and much smaller

what happens to atlas (C1) after birth?
morphology remains unchanged throughout 1st year after birth
but - increases in size (so looks the same just bigger)
in 1st/2nd year ossification occurs in anterior arch
(either as single/paired/multifocal nodules that extend directly from lateral masses)