RA week 2 Flashcards
(165 cards)
thoracic cage made up of?
articulations?
seperated by?
girdle of upper limb? part of throacic cage?
12 pairs of ribs that form lateral walls
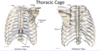
anteriorly = articulates with midline sternum
posteriorly = articulate with 12 throacic vertebrae
seperated by intercostal spaces
girdle of upper limb = scapula and clavicle, not part of thoracic cage
space enclosed by thoracic cage?
thoracic apertures?
thoracic cavity

boundaries of superior thoracic aperture (inlet)?
inferior throacic aperture (outlet)?
superior
- posteriorly = body of T1
- laterally = 1st pair of ribs + costal cartilages
- anteriorly = superior border of manubrium
inferior
- posteriorly = body T12
- anterolaterally (going from lateral to anterior) = 11th + 12th ribs, costal cartilages of ribs 7-10 (costal margin)
- anteriorly = xiphisternal joint


anterior body attached to posterior vertebral arch via pedicle
transverse process function?
what forms spinous process?
note long an sliding arrangement of spinous processes
attachments for muscles
+ articular surfaces for ribs
lamina extend posteriorly and unite to form spinous processes

describe articular surfaces for ribs on T6 and T7
on body of T7 (close to pedicle) - can see superior and inferior demi-facets
- will articulate with head of rib 7 but also rib 8 inferiorly
- head of rib 7 will also articulate with vertebrae above (T6)
articular surface of transverse process
- articulates with tubercle of the 7th rib

types of ribs
classification of ribs

atypical ribs?
ribs 1, 2, 10, 11 + 12

head articulates with body of own vertebrae but also with vertebra above (and with intervertebral disc via the crest)
tubercle - non articular part provides attachment for costotransverse ligament
most curved part of rib body?
costal angle

where is cosal groove?
purpose?
it is an indentation on the internal surface of the inferior border of the body of the rib
provides protection for intercostal vessels and nerves
what makes rib 1 atypical?
what is significant about the bony feature that seperates these grooves?
(pic is superior view)
single facet on head - articulates with T1 only
grooves for subclavian vessels on superior surface (seperated by scalene tubercle)
- scalene tubercle is attachment for anterior scalene muscle of the neck

what makes rib 2 atypical?
(pic is superior view)
has many typical features but is called atypical because it has a rough area on upper surface called = tubersoity for serratus anterior
- attachment site for serratus anterior muscle

what makes ribs 10, 11 and 12 atypical?
(image superior view)
10, 11 + 12 = single articular facet on head, articulates with single vertebra
11 + 12 = very short with no neck or tubercle

divisions of the sternum?
connected by?
manubrium, body and xiohoid process
- manubrium + body connect at sternal angle (manubriosternal joint)
- body and xiphoid process connect at xiphisternal joint

bony features of manubrium?
jugular notch superiorly
clavicular notche son either side of JN = articular surfaces for the clavicles

lateral border of sternum?
articulations?
lateral border has a number of indentations called the costal notches
- 7 costal notches for articulations of costal cartilages of the ribs
1st rib articulates with manubrium adjacent to the clavicular notch
2nd rib articulates at the sternal angle
ribs 3-6 articulate along the side of the body of the sternum
7th rib articulates at xiphisternal joint

level of sternal angle?
rib 2
intervertebral joints?
orientation of articular facets in thoracic region of vertebral coloumn?
intervertebral discs between bodies of vertebrae = secondary cartilagenous joints
synovial plane joints between superior and inferior articular facets (NOT costal facets) - zygapophyseal joint
orientation of articular facets in thoracic region allows rotational movement to occur between the vertebrae

zygapophyseal joint?
synovial plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae
also called facet joints
sternocostal joints?
explain
interchondral joints?
joints between costal cartilages of the ribs and the sternum
rib 1 = primary cartilagenous joint (synchondrosis)
rib 2-7 = synovial plane joints
interchondral joints (joints between costal cartilages) between 6+7, 7+8, 8+9, 9+10
- 6+7, 7+8, 8+9 = synovial plane joints
- 9+10 = fibrous joint

costovertebral joints?
type?
movement?
found between ribs and vertebrae
in image can see 7th rib with head of 7th rib articulating with body of T6+T7
- can also see tubercle of 7th rib articulate with transverse process of T7
-
all of these joints are plane synovial joints
- NOTE: movements will occur at joints formed by head and tubercle (rib moves around an axis that runs between both of these joints)

movement of ribs during respiration?
determined by axis of rotation
- upper ribs = more lateral xis - greatest degree of movement at anterior aspect of rib “pump handle movement”
- ribs 1-6
- lower ribs = more posterior axis - greatest degree of movement at lateral border of rib “bucket handle movement”
- ribs 7-12

rib cage changes in dimension during respiration?
on inspiration rib cage expands along 3 different axis
- sternum + upper ribs move anteriorly and superiorly = increases anterior-posterior dimension
- lower ribs flare out laterally = increases lateral dimension
- diaphragm descends = increases vertical dimension




























































































































