V-Sampling/Estimation-4 Flashcards
(20 cards)
definition:
simple random sampling
简单随机抽样
population中的每个个体都有相同几率被选入样本
definition:
stratified random sampling
分层随机抽样
population is devided into several strata
从每个stratum中按比例随机抽取
definition:
sampling error
the difference between sample statistics and population parameter
如:
sampling error of the mean =
sample mean - population mean
definition:
Sampling Distribution of a Statistic
从总体中随机抽取的、样本大小相同的所有可能性样本的statistics的概率分布
two different forms of data
Time-series data
Cross-sectional data
Central Limit Theorem
实质
条件2
结论2
实质:就关于是所有样本的均值服从怎样的分布
条件:若n>=30, 且总体的均值、方差已知,
结论:则1。sampling distribution服从正态分布,
2。该正态分布的平均值等于总体均值,S2=σ2/n
Standard Error
定义与实质
公式
标准差:样本均值分布的标准差。实质就是如果取n个数的样本,其描述的均值与总体均值的偏差,n越大偏差越小
know population variance:
σx = σ/根号n
unknown population variance:
sx = s/根号n
(即假设样本标准差就是总体标准差)
estimator内涵
3 properties of a good estimator
- estimator: 即estimate formula, 一个计算方式,得出的是一组分布
- unbiasedness: 估计量期望值等于总体参数真实值。E(Xbar) = μ
- Efficiency: (在无偏估计量的基础上)方差最小
- Consistency: 随样本量增大,精确性增加,Standard Error变小
2 approaches for
estimation
- Point Estimate: a single value estimates population parameter
- Confidence Interval Estimate: 总体参数落在某一区间的概率
Confidence Interval Estimation:
公式
confidence interval: Xbar +- k·(σ/根号n)
[Point Estimate +/- k· Standard Error]
(根据normal distribution的置信区间,和central limit theorum推来)
width of confidence interval
and
how to decrease width
sample variance 变小,
number of obervations增加
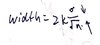
definition:
Level of significance
Degree of Confidence
α
- 显著性水平/置信水平:1-95% = 5%
- 置信度:如“落在μ+-1.96标准差区间内的概率是95%”, 95%
- α: 5%
Student t-distribution
图形及性质5点
- skewness = 0 (symmetry)
- platykurtic than normal distribution,fatter tail 矮峰肥尾
- 变量:Degrees of freedom df = n-1
- 自由度增加,图形收紧,峰变高,趋向于正态分布
- 相同level of confidence水平下,t分布的置信区间比z分布要宽

- z分布,.t分布, .z-Alternative下的置信区间构建
- reliable factor?
z-Alternative: large sample, unknown population variation
equation with z and s
2. reliable factor: 即Z value

confidence interval estimation时,
何时选择z分布,何时选择t分布?
3点
- 方差已知用z,方差未知用t
- 大样本时即使未知方差也可用z(t已趋向于z)
- 非正态分布总体小样本:不可估计
查z分布表和t分布表时
有何区别
t表需知degrees of freedom.
影响confidence interval 宽度的因素
- reliable factor: choice of z or t distribution; choice of degree of confidence
- standard error: sample size
what may be downsides of
bigger sample size?
- 可能会使用observations from another population
- 成本考虑
5 types of bias
- Data-mining bias: 拿偶然当必然,取样与假设检验使用同一数据库。只具有统计学意义
- sample selection bias: 有些数据unavalable
- survivorship bias
- look-ahead bias: 分析当下没有该数据,预估未来数据
- time-period bias:太长或太短(–data mining)
A statistically significant result might not be
economically meaningful if you account
the risk, transaction costs, and applicable taxes


