Uterus/adnexa Flashcards
What is the position of the uterus on this image?

Anteverted retroflexed
-
Version (think vagina): angle b/w cervical axis & vagina.
- In this case, the cervix is angled forward relative to the vagina = anteverted.
-
Flexion (think fundus): angle b/w the uterine body/fundus & cervix at the isthmus.
- In this case, the body/fundus is directed posteriorly, so retroflexed.

- What are the most common GU & non-GU sites for DIE?
- GU: uterosacral ligament.
- Non-GU: rectosigmoid colon.
What structures do the Mullerian ducts form? …and not?
Form: uterus, fallopian tubes, upper 2/3 vagina
Do not form: ovaries
What structure forms the lower 1/3 vagina?
Urogenital sinus
In what direction does fetal uterine cleavage occur?
From bottom to top.
Hence, septae are formed, often extending from the top and only partially to the bottom.
What is Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome?
3 features:
- Vaginal atresia.
- Absent or rudimentary uterus: unicornuate or bicornuate.
- Normal ovaries (so clearly this is a Mullerian issue).
- The kidneys have issues (agenesis, ectopia) in 50% of cases.
What is the issue you need to look out for w/unicornuate uterus?
- 40% will have issues w/the ipsilateral kidney: agenesis.
Uterus didelphys:
- What are the 3 features?
- What is the prevalence of a vaginal septum?
- Didelphys, so two: uteri, cervixes & upper vaginas.
- 75% will have a septum.
Bicornuate uterus:
- In what % is a vaginal septum present?
- Name the 2 types.
- 25% (so less than didelphys, which is 75%).
- Unicollis or bicollis: 1 or 2 cervixes.

What type of cancer is associated w/a T-shaped uterus?
Vaginal clear cell.
From DES exposure.
Septate uterus:
- In what 2 ways, morphologically, is this different from bicornuate?
- What is an imaging pitfall with these and HSG?
- Has a convex fundus (bicornuate has a cleft >1cm); has a fibrous or muscular septum (bicornuate has a myometrial septum).
- On HSG can look like a bicornuate or unicornuate or didelphys, so need MRI.
Is arcuate uterus associated w/infertility or obstetric complications?
NO! Neither.
HSGs:
- Best time to perform & reason?
- 4 contraindications?
- 3 phases of the menstrual cycle & days?
- Proliferative phase of cycle, i.e., day 7-10 (7-14 technically).
- PID, pregnancy, contrast allergy, active bleeding (day 0-7).
- 3 phases:
- Menstrual: 0-7
- Proliferative: 7-14
- Secretory: 14-28

Malignant transformation is a rare complication of endometriosis.
- What is the rate of xsformation?
- What is the most common malignant neoplasm arising from endometriosis?
- 1%
- Endometrioid carcinoma
Which mullerian uterine anomalies are associated w/renal abnormalities?
Unicornuate, didelphys & bicornuate. That is, all those w/abnormal outer contours.
Septate is not!
What is the most constant finding in ovarian torsion?
Unilaterally enlarged ovary. This is true even when there is Doppler flow.
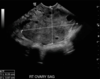
DDx of an abnormally thickened endometrium in a postpartum female?
- hyperplasia
- polyps
- submucosal fibroid
- endometrial carcinoma
If the woman is bleeding then an endometrium >5mm is abnormal & should be sampled.

Outline the recommendations for adnexal simple cysts in post-men women.

- Simple cysts <=1cm are inconsequential; no f/u at all.
- 1-7cm: almost certainly benign; yearly f/u w/US is recommended.
- >7cm: may be difficult to assess w/US; MR or surgical evaluation.
Incidence of dermoid torsion or malignant xsformation?
2%
What will help to eliminate the artifact in this image?

- This is reverberation artifact.
- Occurs when sound reflects off strong acoustic interfaces in the near field, & the returning pulse is strong enough to reflect off the transducer & back into the body so that it interacts w/the same near-field interfaces a 2nd or multiple more times.
- It is often quite obvious in cystic structures.
- Decrease/eliminate by:
- decreasing power output & gain
- reposition the transducer so that the cystic structure is no longer in the near field
Name the most common etiology of abnormal vaginal bleeding in pre- & post-men women.
endometrial polyps



