Core Review GU Flashcards
(35 cards)
Male w/elevated PSA undergoes prostate MR for an observation in the TZ. Which sequence is important for determining the PI-RADS score for this?
T2
- The dominant sequence for TZ interpretation is T2WI.
- Key features for benignity: circumscribed margins & homogeneous hyper- or hypointensity to background parenchyma.
- Malignancy: lenticular shape, non circumscribed margins, moderate hypointensity to background parenchyma & extracapsular extension.

Horseshoe kidneys:
- At what pole are they most often fused?
- Is the isthmic tissue usually functional or not?
- These pts are at risk of what kind of tumour?

- Lower pole.
- Usually functional, less often fibrous.
- Wilms, weirdly enough.
Dx, renal xplant pt w/hematuria.

Iatrogenic injury, AVF.
What is a big differentiator b/w RCC and TCC re: the renal vein.
- RCC often invades the renal vein, and TCC rarely does.
- Both have a propensity for nodal mets.
What are the big 3 tumours that cause IVC tumour thrombus?

- RCC
- HCC
- primary adrenal carcinoma
- Which key imaging feature of a Gartner duct cyst distinguishes it from other cystic lesions in the female pelvis?
- It is located in the anterolateral vaginal wall, above the public symphysis.
- In contrast, Bartholin duct cysts are located in the posterior lateral inferior third of the vagina below the level of the pubic symphysis.

What’s the most common cause of this finding?

- Dx: medullary nephrocalcinosis.
- HyperPTH is the most common cause (40%).
- Next most common is renal tubular acidosis type I - 20%.
DDx?

Dx: renal medullary nephrocalcinosis
HAMHOP:
HyperPTH: most common cause-40%
Acidosis: renal tubular-20%
Medullary sponge kidney
Hypercalcemia/hypercaliuria
Oxalosis
Papillary necrosis
What is the most sensitive US indicator of urinary calculi?
Twinkling artifact.
Prior to Bx of this lesion (an adrenal mass), which lab tests need to be performed?
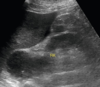
- Plasma free metanephrines & normetanephrines to see if it’s a pheo.
- They have the highest sensitivity for pheo.
- Pheo must be ruled out biochemically prior to an adrenal Bx b/c of the risk of fatal hypertensive crisis during a FNA.
What is the most important factor predicting malignancy within an intrascrotal mass?
Location in or outside the testicle.
- A mass within the testicle is very likely cancer.
- A mass outside the testicle is very unlikely to be cancer.
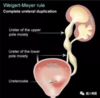
What does the Weigert-Meyer rule predict re: the upper pole moiety?
It will insert inferior and medial.
What is the most common fluid collection seen in renal xplant recipients?
Lymphocele.
- Typically occur 1-3 wks post-xplant.
- They may contain septations, like this one.
- Urinomas are way less common.
- They are usually b/c of breakdown of ureter implantation into the bladder so are generally in close proximity to the bladder.
- Hematomas are common in the early post-op period.
- Urinomas are way less common.

What is the stage of this cervical cancer?

Less than IIB
- There is an intact low-signal intensity ring around the mass on T2W images, so there is no evidence of invasion through the endocervical stroma into the parametrium.
4 types of urachal disorders?
Patent urachus: completely patent urachal tract.
Sinus: blind-ending tract from the umbilicus.
Diverticulum: blind-ending tract from the bladder.
Cyst: a cyst within the urachus that doesn’t connect to the umbilicus nor bladder.

- What is the management for a pt w/pyonephrosis 2dry to an obstructing stone?

- Urgent drainage of the collecting system.
- To evacuate infected uring & allow the Abx to penetrate the infected kidney.
- Lack of decompression of the collecting system has been shown to be associated w/increased mortality.
- Do not manipulate the obstructing calculus first as this can lead to life-threatening sepsis, so this is delayed until after Tx of the obstruction & infection.
In prostate MR, what are specific signs of extracapsular disease?
- Focal capsular bulge.
- Loss of the rectoprostatic angle.
- Soft tissue ingrowth into the neurovascular bundles.
- Measurable extraprostatic extension.
What is the likelihood of osseous mets in a pt w/prostate cancer with PSA <10mg/mL?
<1%
- What is the most common hereditary renal cystic disease?
- What are these pts at increased risk for?

- ADPKD
- HTN
- There is no increased risk for RCC unless they are undergoing prolonged dialysis.
Dx, w/in 1 week of renal xplant?
- Name 2 other causes.

RV thrombosis: diastolic flow reversal w/in intrarenal arcuate arteries (confirmed if there is absent RV flow).
- ATN & acute rejection.
What is the likelihood of malignant xformation of an adrenal myelolipoma?
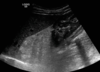
0%!!!!
Mnemonic for common causes of renal papillary necrosis:
NSAID:
NSAIDs
Sickle cell disease
Analgesic abuse
Infection: TB, fungal
DM