URTI/LRTI in Adults Flashcards
(56 cards)
What parasite is a risk when eating cooked or uncooked shellfish / crustaceans?
Paragonimiasis
Paragonimiasis
Paragonimiasis is a food-borne parasitic infection caused by the lung fluke, most commonly Paragonimus westermani. It infects an estimated 22 million people yearly worldwide. It is particularly common in East Asia.
An infection with Paragonimiasis can produce what symptoms?
Cough
Hemoptysis
Explain this chest X-ray.

Consolidation with a perihylar distribution with sparing of the apices and peripheries.
Caused by PCP.
PCP
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Pneumocystis pneumonia causes pneumonia in people with a weakened immune system.
What is PCP (pneumocystis pneumonia) caused by?
It is caused by a yeast-like fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii (PJP).
How do you diagnose pneumonia?

What are the risk factors for community acquired pneumonia?
Immune deficiency
Age
Malnutrition
Steroids
Liver / Renal failure
Diabetes
Prior viral infection
Inflammatory lung disease
What is the prevention available for pneumonia?
What are the two types of this prevention?
Pneumococcal vaccines:
Polysacharide vaccine
Conjugate vaccine
Note: Neither are very good at preventing pneumonia.
How can you tell if someone has been vacinated against TB?
Look on their right deltoid for the BCG scar.
How does pulmonary TB present?
Cough, sputum, fever, weight loss, night sweats, haemoptysis.
What is this a chest X-ray of, explain it.

The chest X-ray is suggestive of a TB infection.
The essential indicator is the cavitatory apical lung disease - seen in this X-ray in the top right lung.
Cavitatory apical lung disease is the classic sign of TB.
What is the diagnosis?
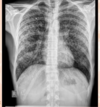
Miliary TB
Miliary TB
Miliary TB is a potentially fatal form of TB that results from massive lymphohematogenous dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli.
Where is the greatest concentration of TB infection in the UK?
London - due to high immigrant populations.
High risk populations include: Indian, African
Mantoux test
The Mantoux test is a widely used test for latent TB. It involves injecting a small amount of a substance called PPD tuberculin into the skin of your forearm. It’s also called the tuberculin skin test (TST).
Measures the immune response - bigger immune response = prior exposure to TB and thus needs to be screened for the disease.
IGRA test
The IGRA test measures the release of a substance called gamma interferon by white blood cells in a sample of blood when the cells are exposed to specific TB antigens.
Clubbing can indicate what?
Lung cancer
Bronchiectasis
Lung abcess
Empyema
Cystic fibrosis
A history of repeated small haemoptysis, or blood-streaking of sputum, is highly suggestive of what?
Lung cancer
Haemoptysis, fever, night sweats and weight loss is suggestive of what?
TB
What is the most common URTI infection and what is it caused by?
Acute coryza caused by rhinovirus infection.
Bordetella pertussis causes what condition?
Whooping cough
What are the symptoms of rhinosinusitis?
Rhinosinusitis typically causes a combination of nasal congestion, blockage or discharge and may be accompanied by facial pain/pressure or loss of smell. Examination usually confirms erythematous swollen nasal mucosa and pus may be evident.




