Unit 4.2 Animal tissues, organs and organ systems and enzymes Flashcards
What is a meant by a specialised cell?
A cell that carries out a particular function (job).
What is meant by differentiation?
When a stem cell changes into a specialised cell.
What is a stem cell?
An undifferentiated cell that can change into any type of cell.
What is meant by an ‘undifferentiated cell’?
A cell that has not yet changed into a specialised cell (e.g. stem cells)
Many similar cells form a…
tissue
Many tissues form an…
organ
Many organs form an…
organ system
Many organ systems form an…
organism
When does differentiation occur in multicellular organisms?
During the development (in the uterus/womb)
What is meant by a multicellular organism?
An organism that is made from many different types of specialised cells.
Why do large multicellular organisms require organ systems?
To transport materials.
To exchange materials.
Name the 3 types of tissue that form the stomach (organ).
Epithelial tissue
Glandular tissue
Muscular tissue
What is the function of epithelial tissue in the stomach?
It covers the stomach like a skin.
What is the function of muscular tissue in the stomach?
It contracts to allow the stomach to churn food.
What is the function of glandular tissue in the stomach?
It secretes digestive enzymes that break down food.
What is the function of glandular tissue?
It secretes enzymes.
It secretes hormones.
Identify the organ system
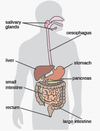
Digestive System
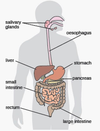
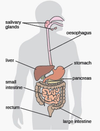
Identify the organ.
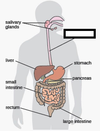
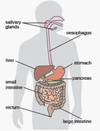
Identify the organ.

Identify the organ.
Identify the organ.

Identify the organ.
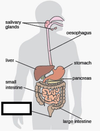

Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.
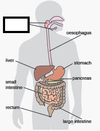
what organ produces digestive juices
glands e.g. pancreas, salivary gland
where in the digestive system does digestion take place?
mouth
stomach
small intestine
amylase breaks down
starch
what is starch broken down into?
glucose
protease breaks down?
proteins
proteins are broken down into
amino acids
fats are broken down by
lipids
fats are broken down into?
fatty acid
glycerol
digested food is absorbed where?
small intestine
water is absorbed where in the digestive system?
large intestine
digestion of starch takes place in which organ?
mouth
small intestine
digestion of proteins takes place in which organs?
stomach
small intestine
Fats are digested in which organ?
small intestine
what type of substance is bile?
alkali
bile is made in which organ?
liver
The role of bile in digestion is?
to neutralise stomach acid
emulsify the fats into droplets
Why is it important that the bile is added as the food leaves the stomach?
to prevent the acid contents denaturing enzymes in the small intestine
What organs in the digestive system does the food NOT pass through?
pancreas
liver
gall bladder
Where does digestion begin?
Mouth
How are the small intestines adapted for absorption?
Folds called villi increase surface area
villi are thin
villi have an extensive blood supply
Where is all the undigested food stored?
rectum
Where does the undigested food leave the body from?
anus
What is the glucose absorbed in digestion used for?
delivered to our cells and used in respiration
What are the amino acids absorbed in digestion used for?
to make new proteins
Where are new proteins made in a cell?
at the ribosomes
organ systems work together to form
organisms
Where is bile stored?
gall bladder
How are proteins different to amino acids?
proteins are large and insoluble
amino acids are small and soluble
How is starch different to glucose?
starch is large and insoluble
glucose is small and soluble
proteases, lipases and amylases are all what type of molecule?
enzymes
what are enzymes made from?
protein
What is an enzyme?
Protein molecule that acts as a biological catalayst
What does an enzyme do in the body?
control and speed up the rate of chemical reactions e.g. respiration
Enzymes are affected by
pH
temperature
True or false enzymes are living
FALSE
You can increase the speed of an enzyme controlled reaction by doing what?
raising the temperature
If the temperature gets too hot for enzymes, what happens to the reaction its controlling?
slows down and eventually will stop
If enzymes get too hot what happens to the enzyme?
they begin to denature (destroyed)
When an enzyme denatures - what does this mean for the enzyme?
The bonds holding the enzyme together break and the enzyme begins to unravel
What shape are enzymes said to have?
globular
Are catalysts used up in the reaction?
No - left unchanged
Name the special site on the enzyme where the reaction takes place
active site
What is the name of the molecule that binds at the active site?
substrate
Can any substrate bind any enzyme?
No - active sites have a specific shape
What makes all enzymes different/unique?
They are all folded into a unique shape
Their active site is specific to the enzyme
When an enzyme binds to the substrate what is formed?
enzyme-substrate complex
pH protease enzymes work best in in the stomach?
pH1-2
Chemical used to detect starch?
iodine
colour change observed if starch is present?
brown to black
In an experiment it is important to control certain variables why?
To make it a fair test
The rate of a reaction is..
a measure of how something changes over time
Digestion breaks down large insoluble molecules into..
small soluble ones (that can be absorbed)
Amylase is made in 3 places - name them
pancreas
salivary gland
small intestine
Protease are made in which organs?
pancreas
small intestine
stomach
Lipases are made in which organs?
pancreas
small intestine
name the acid in the stomach
hydrochloric acid
what does emulsify mean?
break down into tinier droplets
What chemical is used to test for sugars?
Benedicts
How do you test for sugar in a sample of food?
dissolve in water
add benedicts
heat for 5 minutes in a water bath
observe colour change
a sample of food containing a lot of sugar will turn benedicts solution from blue to…
red
A negative test for sugar using benedicts will ….
stay blue (no sugar is present)
The chemical used to test for proteins…
biuret solution
Foods that contain protein include
milk, meat, cheese
starchy foods include
bread rice pasta
to test for proteins you …
dissolve food sample in water
add equal volume of biuret solution
observe colour change
A positive test for protein using biuret will turn
purple/lilac
Lipids (fats) are found in
cheese, chocolate, butter
To test for lipids you…
Grind up food sample
add ethanol
transfer food and ethanol sample to water
look for a white layer/precipitate


