Unit 03: National Income and Price Determination Flashcards
03.01 Classical Economics and Say’s Law
What is the Classical Theory?
Views full employment as the norm of a capitalist economy
- best way achieve price stability, full empoyment, and steady economy = government stay out of economy
- Hands-off approach: Laissez-faire
- Focus long-run: wages, prices, interest rates fully flexable → short run aggregated supply curve more verticle
- prices act rationing system for goods and services
Result:
- Price rise: fewer people willing and able purchase
- Price fall: more people purchase
03.01 Classical Economics and Say’s Law
What contributed the creation of classical economics?
- Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations
- at a time economy at time when factories were in use and labor fully employed
- society = Potential GDP
- economy should be self-regulated
03.01 Classical Economics and Say’s Law
What determines growth in the economy from a classical viewpoint?
Amout of resources and improvements in technology
03.01 Classical Economics and Say’s Law
How does the classical theory say money supply influence the economy?
- Increase money supply directly affect total spending in economy
03.01 Classical Economics and Say’s Law
What is Say’s Law?
Who: Jean-Baptiste Say
- supported Smith’s work /own theory
- The Supply would be traded (demand) for other goods and services. Say and other Classical economics believe that producers only produce goods people willing to buy.*
- “Supply creates its own demand” = Say’s Law*

Fully flexible wages, prices, and interest rates result in an economy that quickly stabilizes.
A proposal that “supply creates its own demand” is called Say’s Law.
Because the economy is self-correcting, there is no need for government involvement.
According to Classical economists, the aggregate supply curve is more vertical
Classical economists believe the economy is inherently stable
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Define short-run aggregated supply.
- Total amount of goods and services that firms are willing and able to produce within economy.*
- short-run, long-run, and immediate short-run
03.02 Aggregate Supply
What is the immediate short-run? how does it relate to supply?
- few days to few months
- input and output fixed
Short-run supply curve: horizontal line at fixed price
03.02 Aggregate Supply
What is the short-run? how does it relate to supply?
- input fixed and output varies
- Prices go up → produce more of producct
- resource prices (especially wages) may not adjust
- SRAS: up-sloping shape
- producers need time adjust changing resource costs
- unemployment recources at lower level = SRAS relatively flat
- Rising levels = produce more until full capacity

03.02 Aggregate Supply
What is the long-run? how does it relate to supply?
- input and output is variable
- price lvel not affect supply
- Supply determined:
- level of productivity
- supply of resources (especially capital and labor)
- Market-forces: self-adjusted to changes
Curve: verticle & economy using all productive resources
- label YF (Y → acronym national income)
- Supply refers to potential output
- Intersection of aggregated demand and SRAS = real or actual output
03.02 Aggregate Supply
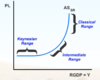
What are the three ranges of the short run aggreagate supply curve?
-
Keynesian (Horizontal) Range:
- recession or depression
- produce more at nearly same price - many unemployed resources
- Keynesian: never at full employment of resources and price level is stable
- reason unemployment result lack of demand
- government step in and create demand
-
Intermediate Range:
- approaching full-employment resources
- healthy economy
-
Classical (Verticle) Range:
- full employment resources
- increase demand results higher prices and little or no more production
- Classical
- economy self-correcting
03.02 Aggregate Supply
What are the 4 determinants of Short-run Aggregate supply?
- Resouce Prices
- Actions by the government
- Political or environmental phenonema
- Productivity
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Determinant of SRAS: Resource Prices (explain and its effect)
changes in input prices raw materials
- Resource prices fall → SRAS increases
- Resource prices rise → SRAS decrease
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Determinant of SRAS: Action by government (explain and its effect)
Changes in business taxes, business subsidies, and business regulations
- SRAS decreases:
- taxes rise
- subsidies fall
- regulations increase
- SRAS increase:
- taxes fall
- subsidies rise
- regulations decrease
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Determinant of SRAS: Political or environmental phenonema (explain and its effect)
Changes in inflationary expectations, wars, and natural disasters
- SRAS decreases:
- inflationary expectations increase
- war or other natural disaster
- SRAS increases:
- inflationary expectations decrease
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Determinant of SRAS: Productivity (explain and its effect)
Changes in technology, worker education, or other factors that affect productivity
- SRAS increases:
- technology increases
- education increase
- productivity increase
- SRAS decrease:
- technology decreases
- workers education decrease
- productivity decrease
03.02 Aggregate Supply
New laws result in an influx of highly educated immigrants. Aggregate supply will
- increase.
- decrease.
- remain the same.
1. increase
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Young adults of today, as a group, are more highly educated than the previous generation. The determinant causing the shift in this scenario is
- price.
- resource cost.
- productivity.
- government intervention (taxes, subsidies, or regulations).
- political or environmental phenomena
- consumer spending.
3. productivity
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Congress votes to substantially increase the minimum wage. Aggregate supply will
- increase.
- decrease.
- remain the same.
2. decrease
03.02 Aggregate Supply
The government cuts business taxes by 10%. Aggregate supply will
- increase.
- decrease.
- remain the same.
1. increase
03.02 Aggregate Supply
Congress votes to increase farm subsidies by 15%. The determinant causing the shift in this scenario is
- price.
- productivity.
- resource cost
- government intervention (taxes, subsidies, or regulations).
- political or environmental phenomena
- consumer spending.
- investment.
4. government intervention (taxes, subsidies, or regulations).
03.02 Aggregate Supply
A new process for producing glass revolutionizes the industry. Aggregate supply will
- increase.
- decrease.
- remain the same.
increase
03.02 Aggregate Supply
A new process for producing glass revolutionizes the industry. The determinant causing the shift in this scenario is
- price.
- productivity.
- resource cost
- government intervention (taxes, subsidies, or regulations).
- political or environmental phenomena
- consumer spending.
2. productivity
03.02 Aggregate Supply
New sources of silicon are located in Wyoming. The determinant causing the shift in this scenario is
- price.
- productivity.
- resource cost
- government intervention (taxes, subsidies, or regulations).
- political or environmental phenomena
- resource cost












