Translation/ Protein Synthesis Flashcards
Describe the structure of tRNA
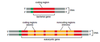
transfer RNA act as adapters that select specific AA and hold them into place on a ribosome for their incorporation into protein. This results in a clover like shape and then is compacted again into an L shape.

How does RNA polymerase start transcription?
when it collides with a DNA and slides down the double helix until it encounters a gene region known as a promoter.
What is the gene region known as a promoter?
a region the contains a specific sequence of nucleotides that lie upstream of the starting point for RNA synthesis.
What is mRNA?
messenge RNA that codes for proteins
What is rRNA?
ribosomal RNA form the core of the ribosomal structure and catalyze protein structure.
What is miRNA?
microRNA regulates gene expression
What is non-coding RNA used for?
-used in RNA splicing -telomere maintenance
tRna match _____ to _____ in mRNA.
Amino Acids ; Codons
What is aminoacyl-tRNA? synthetase?
covalently couples each amino acid to its appropriate set of tRNA molecules. This is known as charging!
What is charging in respects to tRNA and amino acids?
charging occurs when correct amino acids are covalently bonded to their tRNA.
What is genetic code?
The rules by which the nucleotide sequence of a gene, through an intermediary mRNA molecule, is translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein.
Explain what a codon is?
Each group of three consecutive nucleotides in RNA , and each codon specifies one amino acid ex. 5’ AGUGCGAGAA(CCA)3’ –Amino (codon)
Explain what an anti-codon is?
a set of three consecutive nucleotides that bind, through base-pairing, to the complementary codon in an mRNA molecule ex. 5’GCGAGUUGGGACU(GAA)ATCGACCA3’-Amino (anticodon)
What two regions of unpaired nucleotides situated at either end of the L-shaped tRNA molecule are crucial to the function of tRNAs in protein synthesis?
codons and anticodons
Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic replication: