Topic 9 - Lipids Flashcards
How does the polarity of a substance affect its solubility in water?
https://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20080225123318AAbREZ1
List the biological functions of lipids
- Storage of energy
- Insulation from environment
- water repellant
- Buoyancy control and acoustics in marine mammals
- Membrane structure
- Cofactors for enzymes
- Signalling molecules
- Pigments Antioxidants
Describe the importance of lipids
- Structural and function elements of membranes
- Precursors of bioactive compunds (e.g. hormones)
- Regulate enzymatic actions
- Contribute to membrane potential
- Are involved in cell signalling
- some disorders are due to abnormal lipid metabolism
- therapeutic function (steroids, prostaglandins)
What are lipids?
Organic molecules that are characterised by low solubility in water e.g. hydrophobic
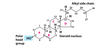
Describe Fatty Acids (saturated & unsaturated)
- carboxylic acids w/ hydrocarbon chains containing b/w 4-36 carbons
- Saturated: no double bonds b/w C’s in the chain. Pack in orderly way
- Monounsaturated: one double bond b/w C’s in the alkyl chain. Pack less orderly due to d/bond kink
- Polyunsaturated: more than one double bond in the alkyl chain

Fatty acid melting point increases with…. and decreases with…. and …..?
Solubility increases with….?
MP & solubility increase w/ chain length
MP decreases w/ unsaturation (number of d/bonds increases)
Fatty acid nomenclature. Describe how to name FA’s
- Remember cis (same side) and trans (different side) -geometric isomers of each other
- Numbering begins at carboxyl C
- A FA 18 C atoms in length w/ no double bonds is 18:0
- A FA 18 C atoms in length w/ 1 double bond at C9 is 18:1(∆9)

Describe naturally occuring FA’s and trans FA
- even no# of C’s
- 1st double bond occurs b/w C9 & C10
- additional d/bonds occur b/w C12-C13 & C15-C16
- D/bonds are in the Cis config (kink)
- Trans FA’s rarely occur in biological systems. Trans d/bond allows a FA to adopt an extended conformation

- Cis 16:1 (∆9)
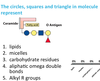
Describe triacylglycerols
- Nonpolar
- majority of FA’s are found as Triacylglycerols
- solid = fat
- liquid = oil
- primary storage form of lipids
- less dense than water and less soluble in water than FA
Describe waxes
- Esters of long-chain saturated and unsaturated FA w/ long-chain alcohols
- Insoluble, high MP
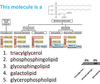
Describe polar lipids
- Amphipathic (hydrophobic & philic groups)
- Major component of biological membranes
- Properties of head group determine surface properties of membrane
- Form micelles, biylayers and liposomes

Membrane lipid structure and function
(see diagram in answer)

Membrane lipid structure and function
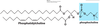
Describe Glycerophospholipids
- Primary constituents of cell membranes
- Head group is charged at physiological pH
- 2 FA form ester linkages w/ 1st & 2nd hydroxyl groups of L-glycerol-3-phosphate
- Unsat. FA are commonly found attached to C2
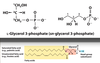
Membrane lipid structure and function
Describe Phosphatidylcholine
- Major component of eukaryotic cell membranes