Topic 7 - Nucleic Acids Flashcards
List the functions of a nucleotide
Energy for metabolism (ATP) Enzyme cofactors (NAD+) Signal Transduction (cAMP)
List the functions of nucleic acid
Storage of genetic info (DNA) Transmission of genetic info (mRNA) Processing genetic info (ribozymes) Protein synthesis (tRNA & rRNA)
What is a gene?
segment of DNA that encodes a protein
Name the two types of nucleic acid
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid)
What is the function of DNA?
Storage and transmission of biological info
What is the function of mRNA?
Messenger RNA: intermediates, carry genetic info from genes to ribosomes
What is the function of tRNA?
Transfer RNA: adapter molecules, transfer specific aa’s to proteins at ribosomes
What is the function of rRNA?
Ribosomal RNA: protein synthesis
Name the 3 components of a nucleotide, and where some of these are attached
Nitrogenous base (N containing) attached at 1’
Pentose (5-membered sugar)
Phosphate attached at 5’

Describe the structural difference b/w DNA & RNA
If only H attached would be deoxyribose
If OH attached is ribose
Picture below shows a ribose

Phosphate group is negatively charged at a neutral pH, and are attached to the 5’ position.
T or F?
True
Name the nucleotides that make up DNA & RNA
Adenine triphosphate (ATP)
Guanine triphosphate (GTP)
**Thymine triphosphate (TTP)
Cytosine triphosphate (CTP)
**Uracil triphosphate (UTP)
**RNA does not have TTP. Has UTP instead, which binds w/ ATP.
Name the two types of pentose (5-membered sugar)
ribose (OH) group
deoxyribose (H) group

Name the two types of nitrogenous bases, what type of structure they are and their components
Purines (adenine & guanine) => lrg, bicyclic
Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine & uracil) =>sml, monocyclic
Draw the basic structure of a purine

Draw the basic structure of a pyrimidine and give some info
All NH groups are attached to sugar
Amino group (HN) wants to give up its H
Carbonyl group (C=O) wants to H bond

Just some general info to read on structure!
- 5’-phosphate of one nucleotide is linked w/ 3’-hydroxyl group of next nucleotide
- Back bone of nucleic acids consist of alternating phosphate & sugar
- Bases are regarded as side groups, hydrophobic
- Ribo-phosphate backbone is hydrophilic and -ve charged
What direction are gene sequences written in?
5’ to 3’ direction
If purine on one strand, other strand must have a pyrimidine & vice versa.
(view pic in answer)
broken line indicates H bonding
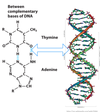
Properties of nucleotide bases affect nucleic acid structure.
T or F?
True
Describe Chargaff’s rule
ratio of pyrimidine to purine is 1:1
i.e. amount of guanine is equal to cytosine
amount of adenine is equal to thymine
What is it about nitrogenous bases that allows them to absorb UV light?
aromatic nature (cyclic structure)
Describe the structure of the double helix
- two antiparallel complementary helical chains
- hydrophilic backbone (sugar & phosphate) are on outside
- purine and pyrimidine bases are stacked inside helix
- Major & minor groove
- Main forces that stabilise helix are: H bonding & base stacking
DNA replication is semiconservative. Why?
Each DNA strand acts as a template for synthesis of a new strand
-progeny DNA consists of one parent and one newly synthesised strand






