Topic 6 - Classes of Enzymes, Michaelis-Menten/Lineweaver-Burk/Eadie-Hofstee, Inhibitors Flashcards
Oxidoreductases
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Electron Donor: Electron Acceptor + Oxidoreductase
Subclasses:
Dehydrogenase
Oxidase
Oxygenase
Reductase
Transferases
Transfer of functional groups
Reactants + Functional group + Transferase
Subclasses:
Kinase
Aminotransferase/Transaminase
Hydrolases
Hydrolysis reactions (a single bond cleavage via addition of H2O)
Compound to be cleaved or formed + Hydrolase
Subclasses:
Phosphotase
Peptidase/Protease/Proteinase
Glycosidase
Lyases
Type 1. Group elimination to change a single bond to a double bond.
Type 2. Breaking a single bond to form two products, one of which has a new double bond.
Reactant + Lyase or Product + Synthase
Subclass:
Synthase: Reverse of Type 2 lyase above
Isomerases
Isomerization (intramolecular rearrangement)
Reactant + Isomerase
Subclass:
Mutase: The apparent migration of a functional group from one position on a compound to another position on the same compound
Ligases
Bond formation coupled to ATP hydrolysis
Reactants + Ligase (or Synthetase)
Subclass:
Synthetase: Formation of a new bond at the expense of ATP/GTP hydrolysis
Dehydrogenase
Transfer of hydride ion
(Oxidoreductase subclass)
Oxidase
O2 is the electron acceptor
(Oxidoreductase subclass)
Oxidase
O2 is directly incorporated into the substrate
(Oxidoreductase subclass)
Reductase
Electron transfer between any 2 compounds
(Oxidoreductase subclass)
Kinase
Transfer of phosphoryl group(s) between one of the adenylates (AMP, ADP, ATP) and another compound
(Transferase subclass)
Aminotransferase (Transaminase)
Transfer of an amino group between compounds
(Transferase subclass)
Transferase subclass
Hydrolysis of a single bond between a compound and a phosphoryl group, producing inorganic phosphate (Pi)
(Hydrolase subclass)
Peptidase/Protease/Proteinase
Hydrolysis of peptide bond
(Hydrolase subclass)
Glycosidase
Hydrolysis of a glycosidic bond
(Hydrolase subclass)
Synthase
The formation of a single bond from two products, one of which had a double bond (The reverse of Type 2 Lyase above)
(Lyase subclass)
Mutase
The apparent migration of a functional group from one position on a compound to another position on the same compound.
(Isomerase subclass)
Synthetase
Formation of a new bond at the expense of ATP/GTP hydrolysis
(Ligase subclass)
Key Note About Enzymes
Enzymes will catalyze reactions in either direction depending on thermodynamic favorability.
Therefore, hydrolases (phosphotases, peptidases/proteases/proteinases, glycosidases), lyases (synthases), and ligases (synthetases) will also catalyze the reverse of the applicable reactions.
Michaelis-Menten Model - 5 Assumptions
- For initial velocity [P] = 0. Therefore, velocity of reverse reaction, E + P –> E-S is 0, b/c V = k-2[E][P] = 0.
- Reaction rate will depend on the rate-limiting step, which is assumed to be E-S —> E + P. Therefore, the actual equation for the intial reaction rate is: V0 = k2[E-S].
- [E-S] instantaneously comes to steady state (not equilibrium b/c this would then be a closed system). Therefore [E-S] remains constant throughout the subsequent time course of the reaction.
- [S] >>>>>>>>>> [E-S]. Therefore, [S] does not change significantly at early time points.
- [ET] = [EF] + [E-S] –> total enzyme = free enzyme + enzyme-substrate complex
Michaelis-Menten Equation
V0 = Vmax[S] / [KM + [S]]
@ Vmax/2, [S] = KM
Vmax = [E] x kcat
Catalytic efficiency = kcat/KM
Lineweaver-Burk (double reciprocal plot)
Original MM Equ: V0 = Vmax[S] / (KM + [S])
Lineweaver-Burk: 1/V0 = (KM/Vmax)*(1/[S]) + 1/Vmax
(y = mx + b)
X-axis: 1/[S], or 1 over the concentration of the substrate
Y-axis: 1/V0, or 1 over the initial velocity. Y-intercept = 1/Vmax when x = 1/[S] = 0
When x = 1/[S] = 0, then y-intercept = 1/V0 = 1/Vmax
When y = 1/V0 = 0, then x-intercept = 1/[S] = -1/KM
Eadie-Hofstee
Original MM Equ: V0 = Vmax[S] / (KM + [S])
Eadee-Hofstee: V0 = -KM(V0/[S]) + Vmax
(y = -mx + b)
X-axis: V0/[S], or initial velocity over the concentration of substrate (will decrease over time)
Y-axis: V0, velocity, Vmax will occur at the Y-intercept when x = V0/[S] = 0
Y-intercept = Vmax when x = V0/[S] = 0
What factors affect Enzyme Activity?
pH
Temperature
Effectors:
- inhibitors (negative effectors)
- positive effectors
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
E + S <–> E-S
- may affect charge of substrate
- may affect charge of amino acids involved in binding substrates
E-S –> E + P
- may affect charge of amino acids involved in catalysis
- disrupt enzyme structure and lead to impaired function
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
- increase the energy of the substrate (increase the activity of the enzyme until…see below)
- denature the protein
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
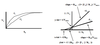
The inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the enzyme. Both cannot bind simultaneously. The inhibitor will appear to change the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate (Alex’s presence appears to change Emily’s affinity for legos).
E + S <–> E-S
E + I <–> E-I (enzyme-inhibitor complex –> makes enzyme inactive)
KI = [E]Free*[I] / [E-I] = reactants/product
a = 1 + [I]/KI, then V0 = Vmax[S] / (aKM + [S])
Graph of Lineweaver-Burk & Eadee-Hofstee:
Lineweaver-Burk: 1/V0 = (KM/Vmax)*(1/[S]) + 1/Vmax
Y-intercept: same, no change in Vmax
X-intercept: change, apparent increase in KM –> will affect the X-intercept by making it less negative (-1/KM –> -1/aKM). Slope will increase for LB (more positive).
Eadee-Hofstee: V0 = -KM(V0/[S]) + Vmax
Y-intercept: same, no change in Vmax
X-intercept: change, apparent increase in KM –> will affect the X-intercept by making it less positive (Vmax/KM –> Vmax/aKM). Slope will decrease for EH (more negative).
Comments: High [S] overcomes inhibition because all of the Enzyme will be bound in the E-S complex. Therefore, greatest inhibition occurs at low substrate concentration. Also: No change in Vmax & apparent increase in KM.
How do mixed inhibitors (noncompetitive inhibitors) affect enzyme activity?
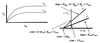
The inhibitor can bind to the free enzyme and also to the E-S complex. The binding constant may be the same for the E-S complex as for free enzyme (KI = K’I, in which it is a noncompetitive inhibitor) or it may be different (KI > or < K’I).
Therefore, will have concentrations of E-S, E-I (same as competitive inhibitor), and E-S-I (same as uncompetitive inhibitor).
KI = [E]Free*[I] / [E-I]
K’I = [E-S][I] / [E-S-I]
a = 1 + [I]/KI & a’ = 1 + [I]/K’I –> then V0 = Vmax[S] / (aKM + a‘[S])
Graph of Lineweaver-Burk & Eadee-Hofstee: Noncompetitive Inhibitor, where KI = K’I
Lineweaver-Burk: 1/V0 = (KM/Vmax)*(1/[S]) + 1/Vmax
Y-intercept: changes, decrease in Vmax –> will affect the Y-intercept by making it more positive. Slope will increase for LB (more positive).
X-intercept: same, no change in apparent KM
Eadee-Hofstee: V0 = -KM(V0/[S]) + Vmax
Y-intercept: changes, decrease in Vmax –> will affect the Y-intercept by making it less positive. Slope will be the same however.
X-intercept: same, no change in apparent KM
EH lines with & without inhibitor will be parallel.
Comments: High [S] cannot overcome inhibition because inhibitor can also bind to E-S complex. Therefore, proportionate inhibition at all substrate concentrations. Also, decrease in Vmax & no apparent change in KM.
How do uncompetitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
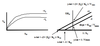
The inhibitor can bind only to the E-S complex (will bind to enzyme after substrate has also been bound).
Therefore, will have concentrations of E-S and E-S-I (same as mixed inhibitor).
K’I = [E-S][I] / [E-S-I]
a’ = 1 + [I]/K’I –> then V0 = Vmax[S] / (KM + a’[S])
Graph of Lineweaver-Burk & Eadee-Hofstee:
Lineweaver-Burk: 1/V0 = (KM/Vmax)*(1/[S]) + 1/Vmax
Y-intercept: changes, decrease in Vmax –> will affect the Y-intercept by making it more positive. Slope will be the same however.
X-intercept: changes, apparent decrease in KM
LB lines with & without inhibitor will be parallel.
Eadee-Hofstee: V0 = -KM(V0/[S]) + Vmax
Y-intercept: changes, decrease in Vmax –> will affect the Y-intercept by making it less positive.
X-intercept: changes, apparent decrease in KM. Slope will also decrease.
Comments: High [S] cannot overcome inhibition because presence of S is required to provide a site for binding of the inhibitor. Therefore, greatest inhibition occurs at high substrate concentration (opposite of competitve inhibition). Uncompetitive inhibition also overlaps in the beginning. Also, decrease in Vmax & apparent decrease in KM.


