Topic 5B Managing Innovation & Growth Flashcards
Why New Product Development is Important
- BCG survey: global innovators generated a 12% premium in past 3 years over non-innovating competitors, and 2% over the past 10 years (a period with several recessions!!)
- Conference board Study: 72% of CEOs said innovation was a top strategic priority; only 55% were satisfied with their financial returns from innovation
- In many industries >50% of sales comes from products introduced in the last 5 years (e.g., electronics, autos, telecommunications)
- >95% of new products fail to achieve an economic return
Impediments to NPD Success (7)
- Risk averse corporate culture
- lengthy development time
- difficulty selecting the right ideas
- uncertainty of outcomes
- rapidly changing technologies
- changing customer needs
- aggressive global competitors
Development Strategies
- Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements
- Minimize Cycle Time
- Control Development Costs
Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements–GOAL
Superior Value proposition
Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements— CHALLENGES
- Identifying most important features
- Balancing Benefits/Costs
- Designing to conflicting segments
Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements— METHODS
- Involving Customers/Suppliers
- Beta testing/ Lead Users
- Crowdsourcing
Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements— Tools
- Conjoint Analysis
- QFD
- FMEA
Maximize Fit with Customer Requirements
Why do companies fail to do this?
•Must offer more compelling features, greater quality, more attractive pricing, better value than competing products
•Why do companies fail to do this?
–no clear sense of what customers value most so overinvest in wrong features;
–overestimate customer willingness to pay for features so stuff product with unwanted features, too expensive;
–Cannot resolve heterogeneity in customer demands so compromise too much, not attractive to anyone
•Customer driven vs. technology driven design
Minimize Cycle Time—Goal
Reduce development cycle time
Minimize Cycle Time— Challenges
- Achieving first to market advantages
- Gaining the efficiencies from faster cycle times
- Avoiding obsolescence
- Controlled speed vs rush
Minimize Cycle Time—methods
- Partly parallel development process
- Project champions
Minimize Cycle Time—Tools
DFM
CAD/CAM
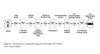
Sequential versus Partly Parallel
Development Processes
Before mid-1990s, most US companies used sequential NPD process
Partly parallel process shortens overall development time, and enables closer coordination between stages.
Control Development Costs—Goal
High ROIC
Control Development Costs– Challenges
- Speed/Cost Risk Optimization
- Benefit/Cost Optimization
- Prioritization