Topic 2 Flashcards
(40 cards)
What is a random experiment?
Any mechanism that produces an outcome that cannot be predicted with certainty in advance.
What is a sample space?
The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
For example, the sample space for tossing a coin consists of head and tails.
What is an event?
A subset of the sample space.
For example, the event of an even number of dots consists of three simple events (i.e., two, four, or six dots).
What is a simple event?
An event of an experiment that contains only one outcome, P(A).
For example, when you toss a coin, the two possible outcomes are heads and tails.
Each of these represents a simple event.
What is a complementary event?
A′ includes all the events that are not part of A.
The complement of five dots on a die is not getting five dots (one, two, three, four, or six dots).
What is a joint event?
- an event that has 2 or more characteristics
- a union or compound event is the probability of observing event A or event B, P(A or B)
- or, if A and B are mutually exclusive, P(A and B)
What do probabilities lie between?
Between 0 and 1:
0 ≤ P(A) ≤ 1
- if P(A) = 1, A is certain to occur
- if P(A) = 0, A cannot occur
What is the sum of the probability of all simple events in the sample space?
One.
Complementary events A and A’ have probabilities that add to one.
Write the formula.
P(A) + P(A’) = 1
or
P(A’) = 1 – P(A)
What is the addition rule of probabilities?
If A and B are mutually exclusive events (that is, A and B cannot both occur), then
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
or
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A and B)
What is the multiplication rule of probabilities?
P(A and B) = P(B|A) x P(A) = P(A|B) x P(B)
What is the conditional rule of probabilities?
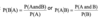
How do we test for independence between A and B?
P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B)
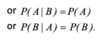
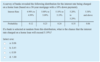
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
a) Give an example of a simple event.

A simple event is described by a single characteristic:
An undergraduate student choosing residential accommodation at UNE.
Or
A student choosing fully-catered colleges.
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
b) Give an example of a joint event.

A joint event is an event that has two or more characteristics:
An undergraduate student choosing a self-catered university flat.
Or
A student selects fully-catered colleges and is an undergraduate.
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
c) If a student is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she:
i. Selected the self-catered university flats?
ii. Selected the fully-catered colleges and is an undergraduate student?
iii. Selected the fully-catered colleges or is an undergraduate student?

i.
P(Selected the self-catered university flats) = 40/150 = 0.267
ii.
P(Selected the fully-catered colleges and is an undergraduate student) = 70/150 =0.467
iii.
P(Selected the fully-catered colleges or is an undergraduate student) = [(85/150) + (100/150)] – (70/150) = 0.767
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
d) Given that a student is an undergraduate, what is the probability that he or she selected fully-catered colleges?

P(selected fully-catered colleges | undergraduate)
= (70/150) / (100/150) = 0.7
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
e) Given that a student selected fully-catered colleges, what is the probability that he or she is an undergraduate?

P(undergraduate | selected fully-catered colleges)
= (70/150) / (85/150) = 0.824
An experiment was conducted to study the choices made by students in choosing residential accommodation at UNE. Suppose 100 first-year undergraduate students and 50 first-year post-graduate students were selected and results are shown below:
f) Are the two events “student group” and “accommodation preferences” independent?

To check whether two events “student group” and “accommodation preferences” are independent, we let:
A = student selected fully-catered colleges
B = student is an undergraduate
Such that:
- P*(selected fully-catered colleges) = P(A) = 85/150 = 0.567
- P*(undergraduate) = P(B) = 100/150 = 0.667
- P*(selected fully-catered colleges and undergraduate) = P(A and B) = 70/150 = 0.467
A and B are independent if P(A and B) = P(A) P(B)
0.467 ≠ (0.567)(0.667), that is: 0.467 ≠ 0.378
Therefore, the two events “student group” and “accommodation preferences” are NOT statistically independent.
A manufacturer receives supplies from two sources – 70% from supplier 1 and 30% from supplier 2. Supplier 1 has a track record of 95% good parts. Supplier 2, with 90% good parts, is not quite so reliable. If a bad part is used in manufacturing process, it will cause serious malfunctions and loss of revenue.
a) What is the probability that the part used is good and is from supplier 1?
P(Supplier 1 and Good Part) = 0.665

A manufacturer receives supplies from two sources – 70% from supplier 1 and 30% from supplier 2. Supplier 1 has a track record of 95% good parts. Supplier 2, with 90% good parts, is not quite so reliable. If a bad part is used in manufacturing process, it will cause serious malfunctions and loss of revenue.
b) Suppose the manufacturer obtains supplies from Supplier 1, what is the probability that the parts are bad?
P(Bad | Supplier 1) = P(B’|A) = 0.05

A manufacturer receives supplies from two sources – 70% from supplier 1 and 30% from supplier 2. Supplier 1 has a track record of 95% good parts. Supplier 2, with 90% good parts, is not quite so reliable. If a bad part is used in manufacturing process, it will cause serious malfunctions and loss of revenue.
c) What is the probability that a manufacturer will receive bad parts?
P(Supplier 1 and Bad) + P(Supplier 2 and Bad)
= 0.035 + 0.030 = 0.065

A company provides health club facilities to its 250 employees. Records for the last year indicate that 110 employees used the facilities. Of 170 males employed by the company, 65 used the facilities.
i. Set up a (2 X 2) table to evaluate probabilities of using the facilities.
ii. What is the probability that an employee chosen at random
(a) is a male;
(b) has used the health club facilities;
(c) is a female and has used the health club facilities;
(d) is a female and has not used the health club facilities;
(e) is a female or has used the health club facilities;
(f) is a male or has not used the health club facilities;
(g) has used the health club facilities or has not used the health club facilities?
iii. What is the probability that someone who uses the health club facilities is male?

(a) P(male) = 170/250 = 0.68
(b) P(used health club) = 110/250 = 0.44
(c) P(female and used health club) = 45/250 = 0.18
(d) P(female and not used health club) = 35/250=0.14
(e) P(female or used health club) = P(female) + P(used health club) - P(female and used health club) = (80/250) + (110/250) – (45/250) = 145/250 = 0.58
(f) P(male or not used health club) = P(male) + P(not used health club) - P(male and not used health club) = (170/250)+(110/250) – (105/250) = 205/250 = 0.82
(g) P(used or not used health club) = P(used health club) + P(not used health club) - P(used and not used health club) = (110/250) + (140/250) – (0/250) = 250/250 = 1
iii. P(male / used health club) = P(male and used health club) / P(used health club) = (65/250) / (110/250) = 65/110 = 0.59

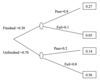
Whether a student will pass the unit depends on whether they have finished the assignment. Given that 30% of the students have finished the assignment. For the student who has finished the assignment, it is 90% probable that they will pass. If they have not finished the assignment, the probability that they will pass is only 20%.
i. Use a tree diagram to find the probability that:
a) the student will fail;
b) the student will fail if he does not do the assignment;
c) the student has not done the assignment and fails.
a) The student will fail.
= 0.03+0.56 = 0.59
b) The student will fail if he does not do the assignment.
= 0.80
c) The student has not done the assignment and fails.
= 0.56