To draw: AA and derivatives Flashcards
1
Q
δ-aminolevulinic acid
A
- endogenous non-proteinogenic amino acid,
- The first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals
- Levulinic acid, or 4-oxopentanoic acid, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH2CO2H. It is classified as a keto acid

2
Q

A
δ-aminolevulinic acid
3
Q
histamine
A

4
Q

A
histamine
5
Q
serotonine
A
- Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin

6
Q

A
serotonine
7
Q
GABA
A
- GABA is primarily synthesized from glutamate via the enzyme glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) with pyridoxal phosphate (the active form of vitamin B6) as a cofactor
- GABA transaminase enzymes catalyze the conversion of 4-aminobutanoic acid (GABA) and 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) into succinic semialdehyde and glutamate. Succinic semialdehyde is then oxidized into succinic acid by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and as such enters the citric acid cycle as a usable source of energy

8
Q

A
GABA
9
Q
dopamine
A

10
Q

A
dopamine
11
Q
acetylcholine
A

12
Q

A
acetylcholine
- name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline.
- Choline: (N+(CH3)3)-CH2-CH2-OH
13
Q
triiodothyronine
A

14
Q

A
triiodothyronine
15
Q
thyroxine
A

16
Q

A
thyroxine
17
Q
epinephrine
A

18
Q

A
epinephrine
19
Q
norepinephrine
A

20
Q

A
norepinephrine
21
Q
carnitine
A

22
Q

A
carnitine
23
Q
taurine
A

24
Q

A
taurine
25
glutathione

26

glutathione
27
DOPA

28

DOPA
29
Alanine

30
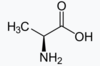
Alanine
31
Arginine

32

Arginine
33
Asparagine

34

Asparagine
35
Aspartic acid

36

Aspartic acid
37
Cysteine

38

Cysteine
39
Glutamine

40

Glutamine
41
Glutamic acid
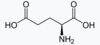
42

Glutamic acid
43
Glycine

44

Glycine
45
Histidine

46

Histidine
47
Isoleucine

48

Isoleucine
49
Leucine

50

Leucine
51
Lysine

52

Lysine
53
Methionine
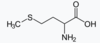
54

Methionine
55
Phenylalanine

56

Phenylalanine
57
Proline

58

Proline
59
Serine

60

Serine
61
Threonine

62

Threonine
63
Tryptophan

64

Tryptophan
65
Tyrosine

66

Tyrosine
67
Valine

68

Valine


