Tissues and Cells of the body Flashcards
Cuadal
toward the tail (coccyx)
Lateral
away from the midline
Medial
toward the midline
Proximal
toward the base
Distal
away from the base
Transverse
horizontal; separates superior and inferior
Sagital
separates left and right
Frontal (coronal)
Separates anterior(ventral) and posterior (dorsal)
Epithelial
arranged in sheets
regeneration

simple squamous epithelium
Bowman’s capsule, alveoli of lungs
reduces friction; controls vessel perm, absorption and secretion

Bowman’s capsule simple swquamous epithelium

stratified squamous epithelium
surface of skin, lining of mouth, throat, esophagys, rectum, anus, and vagina
physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack

stratified squamous nonkeratinizing epithelium in esophagus

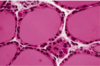
simple cuboidal epithelium
glands, ducts, collecting duct of kidney, thyroid gland
limited protection, secretion, absorption

simple cuboidal epithelium in collecting duct of kidney