Thoracic Wall & Breast Flashcards
What is the difference between the thoracic cage and the thoracic wall?
- Thoracic cage: bones adn cartilage
- Thoracic wall: cage + soft tissue
- skin, superficial fascia, musculature, neurovasculature, pleura & lungs
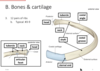
Identify the indicated features & describe their borders

- Superior thoracic apeture (thoracic outlet)
- opening border T1, first rib, first costal cartilage, & top of manubrium
- Inferior thoracic apeture
- lower border T12, rib 12, rib 11 & inferior costal cartilage
- Infrasternal angle
- costal margin
- measured where they are close to joining at the xyphosterno-junction

Identify the indicated features of provided image
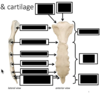
- Xiphoid process
- cartilagenous until age 40
- Costal notches
- 1st entirely manubrium
- 2nd both manubrium & sternal body
- rest are all on sternal body
- NON on xyphoid process
- costal cartilage makes the cage not a fixed structure & is good for breathing purposes

Describe the differentiation between true, false & floating ribs
- True ribs
- First 7 connect directly with the sternum
- False ribs
- 8, 9, 10 connect to the costal cartilage directly above it, rather than the costal cartilage itself
- Floating ribs
- 11 and 12 don’t connect into the rest of the costal cartilage

Which ribs have all of the featues indicted by the image?

- Typical ribs
- 3-9
Identify the features of ribs 1 and 2
What is their classification?

Atypical
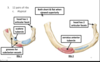
Identify the features of ribs 10, 11 and 12
What is their classification?

Atypical
10 is sometimes a typical rib, but sometiems it only has 1 articular faces
11 & 12 do not really have costal cartilge at sternal ends

Identify the indicatd features of the Thoracic vertibrae


The costovertebral join is a combination of what 2 joints?
How does this joint look for atypical ribs?
- Joint of head of the rib
- synovial
- 2 articular facets of the rib divided by a crest connected to demifafects of 2 adjacent vertibra
- lower articular facet of rib 7 will articulat with superior demifacet of veterbra 7
- costotransverse joint
- articular facet on tubercle of rib & facet on transverse process on same numbered thoracic vertebra
- atypical
- 1 articular facet on head of rib, rather than being on 2 vetebral bodies, only articulate with body of vertebrae of the same number
- 11, 12 have no costotransverse joint
- contributes to mobility

Identify the indicated ligaments in the provided image
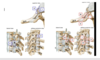
- Joint of head of the rib
- Intra-articular ligament
- crest of the rib to the intervertebral disc
- radiate ligament
- connects the rib to both of the vertebral bodies & IVD
- Intra-articular ligament
- Costotranserse joint
- costotransverse
- space between neck of rib and transverse process of thoracic vertebra
- lateral costotransverse
- most lateral portion of the connection between the transverse process and the rib
- superior costotransvers
- connecting rib to transverse process above it
- costotransverse
- *** remember there is a intratransverse ligament that does not connect to ribs

What movement happens at the following joints?
joint of the head of the rib?
costotransverse joint?
- joint of head of rib
- slight gliding (affects sternum)
- small movements at the head of the rib can mean big movements at the sternal end
- costotransverse joint
- as surfaces become more flattened, the motion changes fom rotation to gliding
- upper: rotate
- raise/lowers sternum like a pump handle
- changes anterior/posterior dimension
- lower: glide (8, 9, 10)
- changes transverse dimension
- raise/lowers ribe like a bucket handle

Describe the relationship between pressure, volume & respiration
- change in volume leading to a change in pressure that leads to air either entering or leaving
- reducing pressure of thorax compared to outside
- air will come in
- increasing pressure of thorax compared to outsde
- air will exit b/c wants to go to the location of lowest pressure

How does the body control volume of the thorax?
- Diaphragm (primary)
- asecends: decreases volume, increases pressure
- descends: increases volume, decreases pressue
- Costovertebral joint
- raising handles (upper & lower ribs): increasing volume, decreasing pressure
- lowering handles (upper & lower ribs): decreasing volume, increasing pressure
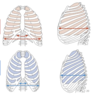
What is flail chest?
- when adjacent ribs are fractured, the ability of the costovertebra joint ito affect thorax dimensions is impaired, limiting respiration

Identify the name & type of the joints indicated by the image

- sternocostal
- synovial except first one
- 1st = (synchondrosis)
- 2nd has 2 joint capsules (one for manubrium & one for sternum)
- synovial except first one
- interchondral
- synovial
- costochondral
- synchondrosis
- Maubriosternal
- symphysis, sometimes completel fuse
- Xiphisternal joint
- synchondrosis (as long as there is cartilage there)
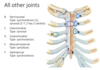
What groups of muscles move the thorax?
- primary
- muscles that pull up (SCM, scalene)
- muscles that pull down (abdominal wall muscles)
- intercostal muscles work together to ix the intercostal space & assist in rib elevation & depresion durign respiration
What muscle is indicated in the provided image?
Attachments?
Spans?
Fiber direction?


What muscle is indicated in the provided image?
Attachment?
Spans?
Fiber direction?


What muscle is indicated in the provided image?
Attachment?
Spans?
Fiber direction?
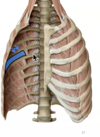

Identify the indicated muscles & features

What muscle is indicated in the provided image?
Attachment?
Spans?
Fiber direction?

- If its crossing a rib then it has to be subcostas
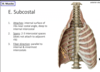
What muscle is indicated in the provided image?
Attachment?
**looking at internal surface of the rib


Identify the veins indicated by black & where they drain to
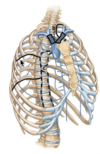
- posterior intervostal
- –> brachiocephalic
- 2 - 4 superior intercostal –>brachiocephalic
- 5 - 7 –> azygos system

Identify the veins indicated by black & where they drain to

- Will have 2 anterior intercostal veins
- 1 - 6 drain –> internal thoracic
- 7 - 9 drain –> musculophrenic
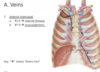
Identify the arteries shown in the provided image

- posterior intercostal
- 1-2 arise off supreme intercostal
- 3-11 arise off thoracic aorta
- the star indicates where it will anastamose with the anterior intercostal artery

Identify the arteries shown in the provided image

- superior anterior intercostal arteries in each intercostal space will anastamose with the posterior intercostal artery
- inferior anterior intercostal arteries in each intercostal space with anastamse with collateral branch of intercostal artery
- lower anterior intercostal arteries will come off of musculophrenic

Identify the branches of the axillary artery


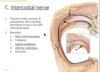
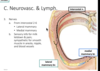
Identify the nerve outline in black

- rami communicantes
- grey & white going to sympathetic trunk
- collateral
- following artery
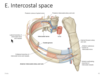
Where do the intercostal lymphatic drain?
either anteriorly to the parasternal nodes or posteriorly to the itercostal nodes
If you are injecting into someon’s intercostal space, how will you aim the needle?
- aim lower b/c want to avoid the larger nerve higher up in the intercostal space
- neurovasculature in costal groove always in order VAN (vein artery nerve)
Where are the following landmarks located with relation to vertebral levels at the end of exhalation?
with relation to costal cartilage?
Scapula?
- Jugular notch:
- Mubrium:
- Sternal angle:
- sternal body:
- Xiphisternal joint:
- xiphoid process:
- Infrasternal angle:
- inferior most palpable part of ribcage:
- Rib 4:
- Rib 8:
- Jugular notch: T2
- Mubrium: T3-T4
- Sternal angle: T4-5 intervertebral disc; costal cartilage 2
- sternal body: T5-T9
- Xiphisternal joint: T9
- xiphoid process: T10
- Infrasternal angle: costal cartilage 7
- inferior most palpable part of ribcage: costal cartilage 10
- Rib 4: medial end of scapular spine & T3 spinous process
- Rib 8: inferior angle of scapulas & T7 spinous process
What the major damage concern for rib 1 fracture? middle ribs? lower ribs?
- rib 1
- subclavian vessels or brachial plexus
- middle ribs
- lung or spleen
- lower ribs
- diaphragm
Describe the general location of the breast
- location
- anterior thoracic wall
- between ribs 2-6
- between sternum & anterior axillary fold
what are teh 2 conventions for organizing areas of the breast?
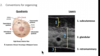
What is the name of the part of the breast that continues up into the armpit. Why is this in important conversation to have with patients?
- axillary process
- should continue breast exams up into this area feeling for masses
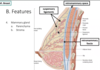
Identify the features of a lactacting breast

- mammary gland: parenchyma

Identify the stromal feature of the breast

What arteries supply the breast & what veins drain it?
- Arteries
- Medial mammary
- off internal thoracic
- lateral mammary
- off lateral thoracic
- Medial mammary
- veins
- superficial & deep plexus of medial ant lateral mammary veings
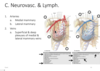
What nerves supply the breast?

Identify the lymphatic nodes that drain the breast

- lymphatics of breast mainy toward axillary node
- specifically central lymphatic nodes on its way to apical

What are common signs of breast cancer?
What are some reasons & considerations for performing a mastectomy?
- Signs will depend on which structure to which the mass is attached
- nipple retraction
- skin edema
- skin dimpling
- mastectomy
- amount of tissue afected by mastectomy depends on type
- surgeon must be award of nearbynerves that can be damaged by procedure
- intercostal nerve
- thoracodorsal nerve
- long thoracic nerve
- reasons
- remove cnacer, prevent cancer, “top” surgery for transgender man


