The nature of electromagnetic radiation part2 Flashcards
The electric component of an electromagnetic plane wave can oscillate in
any direction normal to the direction of wave propagation (which is parallel to the k vector)
A represents

Electric field
B represents

Magnetic field
Suppose that the wave is propagating in the z direction. It follows that the
electric field can oscillate in any direction that lies in the x - y plane
The actual direction of oscillation determines the
polarization of the wave
The actual direction of oscillation determines the polarization of the wave. For instance,
a vacuum electromagnetic wave of angular frequency ω that is polarized in x direction has the associated electric field

a vacuum electromagnetic wave of angular frequency ω that is polarized in x direction has the associated electric field.
where ω=
ω=kc
where ω=kc. Likewise, a wave polarized in the y direction has the electric field

A represents

Horizontal linear polarization
B represent

Vertical linear polarization
Vertically polarized wave
is one for which the electric field lies only in the x-z plane
Horizontally polarized wave
is one for which the elecric field lies only in the y-z plane
(Vertical and horizontal polarized wave )These two waves are termed __________________
linearly polarized
These two waves are termed linearly polarized, since the
electric field vector oscillates in a straight-line
These two waves are termed linearly polarized, since the electric field vector oscillates in a straight-line. However,
other types of polarization are possible
, other types of polarization are possible. For instance, if we combine
two linearly polarized waves of equal amplitude, one polarized in the x direction, and one in the y direction, that oscillate π/2 radians out of phase, then we obtain a circularly polarized wave:
a circularly polarized wave

A represents
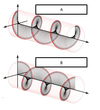
Left hand circular polarization
B represents

Right hand circular polarization
if the x and y components of the electric field in the previous two expressions have different ____________________ then we
(non-zero) amplitudes then we obtain right-hand and left-hand elliptically polarized waves, respectively.
(non-zero) amplitudes then we obtain right-hand and left-hand elliptically polarized waves, respectively. This nomenclature arises from
the fact that the tip of the electric field vector traces out an ellipse in the plane normal to the direction of wave propagation.
A represents

Linear
B represents

Circular
C represents

Elliptical



