The Microbiota of The Gastrointestinal Tract Flashcards
Why does transmit time affect bacterial populations?
Different bacterial growth rates
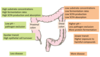
How do the following change as you descend the GIT?
Anaerobic conditions
Bacterial density
Obligate anaerobes
Anaerobic conditions - increase
Bacterial density - increase
Obligate anaerobes - increase
What is meant by a facultative anaerobic bacteria?
Can grow in the presence and absence of oxygen
What is meant by an obligate anaerobe?
Cannot grow in the presence of oxygen
Where are you likely to find facultative and obligate anaerobes?
Stomach and Colon respectively
What does the GIT microbiota do?
- Defence against pathogens (pH inhibition, competition, barrier function)
- Modification of host secretions
- Metabolism of dietary components
- Production of essential metabolites to maintain health
- Development of immune system - immune priming
- Host signalling
What are the factors that determine the composition of the dominant bacteria along the GIT?
different oxygen concentrations, different pH, different transit time
What do the GIT microbes grow on?
Fibre we eat in foods like fruit, vegetables, pulses and whole grains to convert it into thousands of different products
•GIT microbes can also use endogenous
(host-derived) substrates for growth
(apparently energy absorbed from these food sources is absorbed in the large intestine)
What is the benefit to our health if we include dietary fibre in our diet?
Improves faecal bulking, eases passage, results in shorter transit time
Contains important phytochemicals, anti-oxidants and vitamins
What is the result of bacterial fermentation?
Releases additional phytochemicals
Maintains slightly acidic pH
Resistance to pathogens is increased as a result of increased commensal bacterial population and pH
Supplies essential short chain fatty acids and branched chain fatty acids
What are the main short chain fatty acids?
Butyrate
Propionate
acetate
What is the function of butyrate, propionate, acetate?
Butyrate - Epithelial cell growth and regeneration
Propionate - gluconeogenesis in the liver,
satiety signalling
Acetate - lipogenesis
What are the major products of carbohydrate metabolism?
SCFA
Gases (CO2, H2, CH4)
Whar are the major products of protein metabolism?
Branched short chain fatty acids
Gases (ammonia) hydrogen sulphide
Phenols, indols, amines
Where are most of the short chain fatty acids produced?
In the ascending colon - hence the slightly acidic environment
What is the pH of the descending colon?
pH neutral
Give examples of utilised materials by bacteria and examples of products
Potential substrates: Polysaccharides, prebiotics, mucin
Potential products: SCFA’s, lactate
Describe the barrier effect that protects the host against pathogens?
Colonisation of pathogens is prevented as a result of large numbers of indigenous microbiota
It also keeps in check potentially pathogenic bacteria that are normally resident at low levels
What does the mucus layer form a barrier inbetween?
The luminal bacterial population and the produciton of epithelial cells
What is the function of the inner mucus layer?
Prevents bacterial penetration
What is in place to deal with the few bacterial cells that penetrate through the epithelium?
The immune system
(Dendritic cells, IgA, macrophages)
Which bacteria prevent the adhesion / colonisation of pathogens?
Those that are close to the epithelium

What might cause a disruption in the structure and or function of the GI tract?
IBD - reduces the barrier effect.
What is the effect of a disrupted mucus layer barrier?
Weakens the protection of the gut epithelium, enables the bacteria to bind to the gut surface and potentially cause inflammation.
Describe some of the differences between Proximal colon and distal colon.
Relevant Learning intention (Understand why there are differences in bacterial communities through the GIT)
What is the immune function of the gut?
(No relevant learning intention)
Surface is in constant interaction with the external environment
Must be able to:
- Respond to pathogens
- Inhibit immune response to self proteins, dietary antigens and the commensal microbiota
How does the innate immune system detect bacteria that do not penetrate?
Pattern recognition receptors
Toll like receptors
What is the activity of pattern recognition receptors?
Molecules that are associated with pathogens, microbes or cell components are detected and binded by PRR’s
Results in the release of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and co-stimulatory molecules.
What is the activity of toll like receptors?
Specifically recognise bacterial components
When do autoimmune diseases occur?
When the host immune system can no longer distinguish between detrimental pathogens and commensal bacteria
What is meant by dysbiosis?
Microbial imbalance
What is the result of dysbiosis of the gut microbiota?
Inflammation
What are some of the benefits of SCFA’s? Which are detected by receptors in the gut epithelial cells
Learning intention (Explain why the presence of/products of bacteria are important for a healthy gut)
Inhibits fat accumulation
Improves insulin resistance and satiety signalling to brain
Suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis

How does microbial diversity change with age?

Summary:
How do resident bacteria prevent pathogen colonisation?
lowering pH, creating a physical barrier, prime immune system,
produce active compounds that kill incoming pathogens



