Liver Structure and Function Flashcards
What are the lobes of the liver?
- 2 Major lobes: Right > Left
- 2 Minor lobes: Caudate, Quadrate
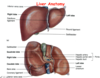
What blood vessels exit/enter the liver?
hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery
What else other than blood vessels exit/enter the liver?
•, lymphatic vessels, ducts (right/left hepatic ducts Þ common hepatic duct), nerves (hepatic nerve plexus) via Porta on inferior surface
What is the common bile duct composed of?
Common hepatic duct + cycstic duct of gall bladder
What joins onto the common bile duct?
Pancreatic duct - forming the major duodenal papilla (sphincter of oddi)
What is the liver covered in?
Connective tissue capsule and visceral peritoneum except for bare area.
The bare area is surrounded by coronary ligament and is found on the diaphragmatic surface
Define porta hepatis
The porta hepatis or transverse fissure of the liver is a short but deep fissure, about 5 cm long
What structure provides support in the liver?
The connective tissue capsule provides a branching network of septa into the body of the liver
(·Vessels, ducts and nerves follow septa throughout liver)
How are hexagonal lobules formed?
Septa divide
What is the portal triad?
Hepatic portal vein
Hepatic artery
Hepatic duct
Where are portal triads located?
At the corner of each hexagonal lobule
How does the blood from a lobule enter the IVC?
Travels to the central vein of the lobule - hepatic vein - IVC
Define Hepatic chords, Bile canaliculus and hepatic sinusoids
Hepatic chords are chains of hepatocytes that radiate out from the central vein like spokes on a wheel.
Cannaliculi ie between cells within each chord
Hepatic sinusoids are blood chanels that fill the space between hepatic chords

What do the bile cannaliculi eventually form?
The bile duct
What feeds into hepatic sinusoids?
The hepatic portal vein, the hepatic artery and some of the products of hepatocytes (basically everything that needs to go to the central vein)
What is the direction of transport of materials from the hepatic sinusoids?
Some travel to the central veins
Others travel to the hepatocytes (probably excess nutrients and toxins)
What is the transport from the central vein?
Travels to hepatic veins
What is contained within the blood coming from the hepatic portal vein?

What is contained in the blood coming from the hepatic artery?
O2 - rich nutrient depleted blood
What substances are found within the hepatocytes?
Bile
Nutrient storage
Glycogen
Fat
Vitamins (B12,A,D,E,K)
Copper
Iron
Nutrient interconversion
Detoxification
What is the movement of bile that has been synthesised by hepatocytes?
Travels to cannaliculi to hepatic ducts
What is the alimentary role of the liver?
Production and secretion of bile
What are the components of bile?

What is responsible for the formation of Bile acid, Lethicin, Cholesterol, Bile pigments, toxic metals?
Secreted by hepatocytes



