The Limbic System, emotion, the hypothalamus and appetites Flashcards
(40 cards)
What are the main types of sensory inputs that can be put into the cortex?
- visual
- auditory
- feel
- memory
- context
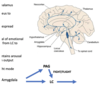
What are the core components of the limbic system
- Amygdala – emotion
- Hippocampus (+ cortex) [H. formation] = memory
- Limbic cortex – cingulate gyrus/insula

What is the function of the limbic system?
processes emotion and related brain activity, memories, environmental cues and state of the individual and acts on this information to maximise survival strategies
What are the effectors of the limbic system?
- Hypothalamus
- Brainstem structures
**drive responses

Describe the amygdala
- Grey matter blob with central, cortico-medial and basolateral nuclei

What is Klüver-Bucy Syndrome and what are the common features?
- Rare syndrome in humans that produces behavioural impairment
- Associated with damage to the anterior temporal lobes
- Common:
- Hyperorality
- Placidity (lack of fear)
What is thought to cause Klüver-Bucy Syndrome?
- Herpes encephalitis
- Trauma
- Tumours
- Hypoxia
- Pick’s disease
What is amygdala activated by to generate an emotional response?
- Electrical stimulation leads to anxiety and fear
- Fear activates central nucleus (and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST))
- fMRI –> (fear can be due to real imagined object and is context dependent; stria terminalis connects amygdala with BST and is one of a number of connecting tracts assigned to the limbic system)

In what disorders are the centres of the amygdala enhanced?
anxiety disorders
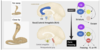
Describe the inputs into the amygdala
- stimulus
- take a fast tract pathway via thalamus - doesn’t reach consciousness (e.g. subliminal short route)
- Longer route via cerebral cortex (long route e.g. visual cortex)
- Concept - via cerebral cortex
- Context - via hippocampus
- Inputs go into the lateral nucleus of the amygdala
- Outputs from the central nucleus

Describe the learning aspect of the amygdala
- Noise or scene associated with a fear stimulus can elicit fear
- This extends to context such as the place or situation in which the fearful stimulus occurred
- This learning happens in amygdala (distinct from hippocampal memory)
- Basolateral amygdala compares incoming sensory stimuli (conditioned stimuli, CS e.g. tone, light, smell or context) to previously learned aversive stimuli (unconditioned stimulus, US, e.g. fear/pain)
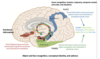
What are the main outputs of the amygdala?
- output to hypothalamus via stria terminalis
- output to a variety of brainstem centres
- Periaqueductal grey matter (PAG)
- Parasympathetic (colitary nucleus, dorsal vagal nucleus)
- Ventral tegmental area

Summarise the functions and actions of the amygdala
- Controls emotional reactions (particularly threat/fear) via effectors (hypothalamus, brainstem through the autonomic nervous system, endocrine and motor system)
- Emotional learning resetting according to threat level and experience (memory)

What is responsible for higher order functions in evaluating the survival value of an emotional response?
Cingulate Gyrus
What components form the limbic cortex?
Anterior (ACC) and Anterior Portion of the Middle (MCC) involved in emotions

What connections do the ACC and MCC have for emotion?
- ACC = direct communication with amygdala, and to effectors in the brainstem (behaviour/ANS)
- MCC = to motor cortex (movement/behaviour)

Describe the functioning of the anterior cingulate nucleus in encoding basic emotion
- Anterior cingulate nucleus encodes basic emotions; happiness, sadness and fear and emotional memory
- Anterior cingulate has a top down influence – works to recode the amygdala
- Computes relevance/outcomes – drives appropriate behaviour
- Provides conflict resolution (dorsal ACC e.g. self V non-self in threat)
- Part of pain network – thalamus, primary somatosensory area and insula
What are the effector pathways of the limbic cortex?
- Anterior and Middle Cingulate regulate complex interaction between unpleasant cues/pain emotions and avoidance behaviours and response. Work through amygdala and firectly to brainstem/motor cortex
- Motor reactions complex and content dependent (approach/avoidance behaviour; desire to leave the room; vocalisation: facial expression; kissing; lip puckering; pushing)
- Specific zone for driving face muscles
- Direct outputs from ACC to autonomic system (BS – dorsal motor nucleus of X and the nucleus of solitary tract). Also, indirect via the amygdala
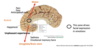
What is the primary limbic cortex and what is its function?
ACC (+ some MCC) - higher order processing of emotion (top down with amygdala)
- Has reciprocal connections with the amygdala
- Heavy direct connections to autonomic centres including brainstem (bypass amygdala)
- Attentional system, monitors conflict and resolves it
- Pain activates complex interaction with emotion here
- Motivates behaviours, mediates orientation towards or away from emotional stimuli
- Recodes value of stimulus on amygdala

What is the function of the insula?
- Works with the ACC in evaluating emotional contexts – role in empathy
- encodes “emotional awareness”

What is the input for the insula?
Visceral information including pain
**Patients with lesions have defects in awareness of other people’s pain (empathy)
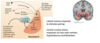
Draw a diagram highlighting the function of the amygdala along with the limbic cortex

Describe PTSD in the Limbic System
- Part of ACC is hypo-responsive in PTSD
- Reduction in size of ACC
- Amygdala becomes hyper-responsive to trauma related stimuli
- Top down control of amygdala by ACC is therefore missing in PTSD
Summarise the functions and actions of the cingulate gyrus
- Emotion response regulation coordinated via connections with amygdala
- Makes prediction about negative consequences resolves conflicts
- Top down regulation “recodes” the amygdala processing/responses
- Drives conscious responses to unpleasant experiences
- Drives avoidance behaviours and motor such as facial expression (from MCC to motor cortex
- Also, direct influence on limbic effectors (ANS) by-passing amygdala
- Works with insula which provides wider context of awareness to unpleasant especially visceral stimuli (empathy; pain)