Ascending Pathways Flashcards
(40 cards)
What is the modality and features of:
Hair follicle receptors:
- Touch
- Rapidly adapting

What is the modality and features of:
Merkel endings
- Pressure, low frequency vibration
- Slowly adapting

What is the modality and features of:
Meissner Corpuscles
- Light touch
- Rapidly adapting

What is the modality and features of:
Pacinian corpuscle
- Vibration and Joint position sense (JPS)
- Rapidly adapting

What is the modality and features of:
Ruffini endings
- Skin stretch, pressure and JPS
- Slowly adapting

What is the modality and features of:
Nocioceptors
Pain
Free nerve endings
What is the modality and features of:
Muscle Spindles
Muscle length and proprioception
What is the modality and features of:
Golgi Tendon Organ
Joint position sense
Slowly adapting
Describe the sensor response in comparison to an action potential
Slow
Describe the concept of lateral inhibition
- Each sensory neuron has a receptive field
- Dendrites are dense at the centre and diffuse at the periphery
- Stimuli at the centre of the field activate more dendrites than at the periphery and so cause faster firing

What is the main function of lateral inhibition?
Sharpens discrimination between two points

How does lateral discrimination translate to sensation?
(draw a diagram)

What is the function of the 1st neuron in the sensory pathway?
(take signals from the periphery to the CNS)
1st neurons in the ascending pathway “sense” and exit from their cognate dermatome zone then feeds into a chunk of spinal cord that “belongs” to that body segment
Draw a diagram illustrating somatic sensory input

Describe the action of spinal cord segements
Sensory rootlets come from a dermatome
- Internally indistinct/functionally important
- Serves body segment (dermatome/myotome)
- Lower segments much higher than their level of exit therefore the cauda equina
How many pathways travel to the cerebral cortex for concious sensation
Two

Both pathways have 3 neurons, relay in thalamus and cross over to the opposite side of the brain
Do the dorsal and anterolateral pathways cross the spinal cord?
Yes
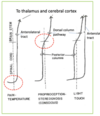
What is the function of the dorsal colum (medial lemniscal pathway)?
Vibration and conscious position sense - two-point discrimination/fine touch
Describe the pathway of a sensory signal coming from the leg to the brain (below T6) travelling in the dorsal column
- 1st neuron – DRG, spinal cord ascends on SAME side to medulla
- 2nd neuron – medulla, axon crosses and ascends to thalamus
- 3rd neuron – in thalamus ascend to cerebral cortex (postcentral gyrus)

Describe the pathway of a sensory signal coming from the arm to the brain (above T6) travelling in the dorsal column
- Arm fibres more lateral in spinal cord
- 2nd neuron in separate medulla nucleus to neurons “servicing” the leg
- 3rd neuron in thalamus and projects to cerebral cortex

How is the primary somatosensory cortex arranged?
- Somatotopy in the primary somatosensory cortex
- Topographical arrangement of the body representation across the sensory cortex

Cortical functions of the dorsal column
- To determine the shape of an object (without sight)
* Proprioception from the finger joints and fine discriminating touch provides a very accurate model of any object that is handled - To determine the texture of an object (without sight)
- Texture is determined by vibration and slip (Meissner) receptors as well as fine discriminating touch.
- Note pleasure can be associated with this pathway
**Requires the somatosensory area association area in the parietal lobe is functioning properly/normally
Astereognosis
is the inability to identify an object by active touch of the hands without other sensory input, such as visual or sensory information.
Stereognosis
the mental perception of depth or three-dimensionality by the senses, usually in reference to the ability to perceive the form of solid objects by touch.










