The gonads 1 Flashcards
What enzyme converts Adrostenedione into oestrone?

AROMATASE
What are the names of the Sex Steriods produced in Men by the Gonads?
Sate the name of the sex steriods produced in large amounts and the sex hormones produced in much smaller amounts in the gonads?
Androgens- Large
Oestrogen , Progestogens- Small

In response to … stimulation, the Thecal Cells will start steroid hormone synthesis and produce the ……………….
In response to LH stimulation, the Thecal Cells will start steroid hormone synthesis and produce the Androgens

What does inhibin do?
INHIBIN - feeds back on the axis and inhibits FSH secretion

What is the main hormone during the luteal phase?
LUTEAL PHASE - PROGESTERONE is the dominant hormone

The spermatozoa produced travel down to the collection in the …………. …………. where they are concentrated and drained by the …………. …………… into the …………… where they are stored
The spermatozoa produced travel down to the collection in the Rete Testis where they are concentrated and drained by the Vasa efferentia into the epididymis where they are stored

What enzyme converts progesterone to 17-OH Progesterone to Androstenedione?
The same enzyme is used for both reactions

17,20-lyase
17α-hydroxylase
They are both the same enzyme
What converts 17-OH progesterone to 11-deoxycortisol?

21α-Hydroxylase
When event signifies the start of the menstral cycle?
Historically taken to begin on the first day of menstruation

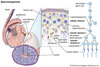
Describe the embryogenesis of gonads?
Name the cells present in the undifferentiated structure which forms into the gonad and state what cells they become in the testes?
Ovaries and Testes develop from the same undifferentiated gonad. By about 6 weeks of embryogenesis this undifferentiated structure consists of primordial germ cells, support cells and laydic cells and it is a gene on the Y chromosome- the SRY gene that triggers the differentiation into the testes. So it triggers the these primordial germ cells to differentiate into spermatogonia, the support cells differentiate into sertoli cells and the steriodigenic cells differentiate into leydig cells. In the abscence of the Y chromosome the Ovaries will form

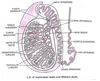
Cross section of a seminiferous tubule

Under the influence of FSH, the follicles will get bigger until they eventually get to their maximum size which is the …………. Follicle which is ready for ovulation
Under the influence of FSH, the follicles will get bigger until they eventually get to their maximum size which is the Graffian Follicle which is ready for ovulation

Postaglandins help with the expulsion of menses
NB: The follicle most sensitive to FSH do not undergo ATRESIA

The endometrium is the lining of the uterus and contains a ……………. ……………… layer and a …………… …………… layer
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus and contains a superficial epithelial layer and a deeper stromal layer

How much cooler is the scrotom to the core body temperatureand why is this important?
The scrotum is 2-3 degrees cooler than core temperature - which is critical for spermatogenesis
Overview

Proliferative - Oestradiol is the dominant influence - causes proliferation of the endometrium
Endometrium thickens - it stimulates mitosis and the glands which are initially straight becomes enlarged and they coil - increased blood supply
Secretory - Progesterone is the dominant influence
In the secretory phase, oestrogen and progesterone are secreted
The glands become secretory, they dilate and produce large amounts of glycogen and mucopolysaccharides and other things
The mucosa is engorged with blood
If fertilisation doesn’t take place, oestrogen and progesterone levels fall so they no longer stimulate the epithelium
You get spasm of the blood vessels, tissue becomes necrotic and the blood is shed
Progesterone reverses the effects of oestrogen - it reduces the proliferation that oestrogen causes by reducing oestrogen receptors
Progesterone also increases the secretory activity of the cells in the myometrium (middle layer of the uterus lining) - glands become wider and produce various substances which make the environment suitable for implantation to occur

What is Spermatogonia?
A spermatogonium (plural: spermatogonia) is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogoniaundergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.

Where in the testes does spermatogenesis occur?
Spermatogenesis takes place in the SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES of the testes

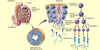
The dominant follicle will produce large amounts of ……………….
The dominant follicle will produce large amounts of oestrogen

Thecal cells do NOT have the ……………….enzymes to convert ………………….. to oestrogen
The Granulosa cells have …….. Receptors and stimulation of these cells will stimulate the ………………. enzyme which convert these ……………..into oestradiol
Thecal cells do NOT have the aromatase enzymes to convert androgens to oestrogen
The Granulosa cells have FSH Receptors and stimulation of these cells will stimulate the aromatase enzyme which convert these androgens into oestradiol

As these cells develop they towards the lumen and are released into the lumen

What effect does oestrogen have on the endometrial cycle?
It is the oestrogens (produced in the follicular phase) which cause the effects that we see in the proliferative phase in the endometrial cycle
Oestrogen causes proliferation of the endometrium - there is an increase in mitosis and an increase in the progesterone receptors (which acts later in the cycle) and an increase in oestrogen receptors
The endometrium gets thicker, the glands get bigger and the blood vessels get longer

What effect does progesterone have on the menstral cycle?

We have follicles with the oocyte that is stuck in the early stage of meiosis
The follicle will develop over embryonic life and will develop to this pre-antral stage
Up until the pre-antral stage, gonadotrophins are NOT needed
To develop any further requires FSH (to get to early-antral stage)
What happens if the FSH levels are not at a high enough level?
If FSH isn’t at a high enough level to continue the development they will undergo atresia