The Abdomen: Anterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
Anterior abdominal muscles (from superior to inferior)
External abdominal oblique
Internal abdominal oblique
Transversus abdominis

Ant. abdominal wall layers of superficial fascia
Camper’s: superficial layer
Scarpa’s: deep layer

Lymph drainage (in relation to umbilicus)
Above: parasternal and anterior diaphragmatic nodes
Below: superficial inguinal lymph nodes

Venous drainage to major vessels occurs at___
axillary and femoral veins
External oblique muscle characteristics (origin/insertion/location/action/innervation/blood supply)

Internal oblique characteristics

Transversus abdominis characteristics

The following structures mark which vertebral level?
Umbilicus
Slightly superior to pubic bone
Labia majora/scrotal sac
Umbilicus: T10
Pubic bone(just superior): T12
Labia majora/scrotal sac: L1
Arcuate line
Point at which posterior rectus sheath becomes transversalis fascia

Name the structures that make up the following sheaths:
Posterior rectus sheath
Anterior rectus sheath
Transversalis (endoabdominal fascia)
Anterior rectus sheath: aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique
Posterior rectus sheath: aponeuroses of internal oblique and transversus abdominus
Transversalis fascia: posterior rectus sheath at arcuate line

What blood vessels primarily supply the anterior abdominal wall?
Superior and inferior epigastric vv. and aa.
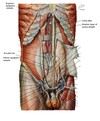
Location of Superior epigatsric vv and aa.
Deep to anterior rectus sheath

Location of inferior epigastric vv. and aa.
Deep to posterior rectus sheath

Aortic coarctation and implications
Narrowing of the aorta; inf. epigatsric vessels and intercostal arteries compensate to get blood the limbs
Spermatic cord
Formed by ductus deferens (males) (ties gonad to scrotal sac)

What is the spermatic cord equivalent in females?
The round ligament of the uterus
Abdominal wall components and what they form

Inguinal canal
Formed by:
Lateral: inguinal ligament
Anterior and superior: ext abdominal oblique aponeurosis
Posterior: anterior superior iliac spine

Superficial inguinal ring
Formed by medial and lateral crus
In males, what structure comes out of the superficial inguinal ring? What is the equivalent in females?
Spermatic cord
Round ligament of the uterus
Deep inguinal ring
Deep to where the transversus abdominis muscle archesover the spermatic cord or round ligament
Formed by meeting of transversalis fascia and internal spermatic fascia
Conjoint tendon
Formed by lower tendinous parts of internal aponeurosis and transversus abdominis aponeurosis
Inserts at the pubic crest and pectineal line

L1 nerves
Ilioinguinal and iliohypogatsric nerves
Ilioinguinal nerve
Travels along spermatic cord/round ligament
Exits at superficial inguinal ring


