Test Questions Flashcards
(58 cards)
Describe the electrical activity occuring during the PR interval
all elecrtical activity

What part of the AP curve corresponds to the ST segment?
Phase 2
plateau phase
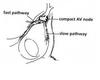
What two pathways can be localized within Koch’s triangle?
Fast: Anterior
Slow: Posterior
Name three major deflection on the HIS electrogram
- A
- H
- V
Which ion occurs during phases 1, 2 and 3?
Potassium
What is extrastimulus pacing which demonstrates the longest coupling interval for which a premature impulse is blocked or fails to propagate through that tissue?
Effective Refractory Period
What is the longest coupling interval to be associated with a blocked premature stimulis?
ERP
What structure extends from the coronary sinus os to the superior aspect of the septum?
Tendon of Todaro

What’s the most common mechanism for arrhythmias?
Reentry
Which phase correlates with the relative refractory period?
Phase 3
Name the three borders of the triangle of Koch
- Septal leaflet of the Tricuspid
- os of the coronary sinus
- Tendon of todaro

How do you measure the AH interval?
onset of the A to the onset of the H on the HIS
Name 2 uses for an EP catheter
- pacing
- recording
Which fluoro view shows the long axis of the ventricles?
RAO
Where is Na+/K+ pump is activated?
Phase 4
What is the longest coupling interval that delays conduction?
RRP
Which ion triggers cardiac muscle contraction?
Calcium
Which ion is responsible for depolarization in a cardiac pacemaker cell?
Calcium
What is the period of time when the initiation of an action potential is impossible no matter how strong the stimulus?
ARP
What percentage of people have the AV nodal artery arising from the RCA?
85%
What is the inherent firing rate of the AV node?
40-60 BPM
How does the electrical conduction travel from the right atrium to the left atrium?
Bachmann’s Bundle
Atrial kick accounts for how much blood into the ventricles?
20-30%
Phase 3 correlates with what on the ECG?
T wave








