test 3 Flashcards
(77 cards)
The _____phase has a greater tendency than the gas to wet the solid.

why is 2 phase analysis satisfactory

what are the curved lines

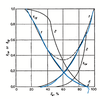
relative permeability

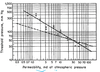
describe this chart


If the porous medium is assumed to be a bundle of capillary tubes of various radii, then the capillary-pressure-saturation curve relates ____________

describe how to measure kr in the lab using the unsteady state method

how is permeability of oil reported with the saturation of oil is 60% and water 13%

what is the drainage curve

what is the equation for gas saturation at the outflow during the Welge method of measuring kr

describe the shape of the graph


Its not possible to measure ______ directly in the reservoir

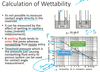
a wettability number of zero means what

________ is a generalized form of Darcy’s law which describes simultaneous flow of two or more immiscible fluids.

what is point 3 on this curve


•Darcy’s law, originally formulated and developed to apply when the porous medium was ___saturated with a ____ , ______ fluid.

what are the assumptions in the Welge method of measuring kr

if you were to graph the size distribution of the poor size, what would be the distrbution for each of the graphs below

unimodel/bimodal vs. trimodal+

effective permeability is measured in the ___

As the saturation of the nonwetting phase increases, the average pore size saturated with wetting fluid becomes …

The area under the right curve gives you what?

permeability of sample
what is point 5 on this curve


At lower water saturations the oil occupies _____ of the smaller pores.

a wettability number of 1 means what

describe this graph