Test 2 Flashcards
(134 cards)

supinator
Types of exocrine glands
Serous- viscous solution
Mucous- mucous solution
Mixed- both viscous and mucous
Transverse tubules
T-tubules

stratified squamous non-keratinized
Terminal cisternae
Widened ends of sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcomere
Functional unit of skeletal muscle, sarcomeres are connected in series to make myofibrils. About 10,000 sarcomeres make myofibrils, each sarcomeres contracts shortening length of myofibril.

neuromuscular junction
Describe the structure of dermis
• Composed of connective tissue
• Highly vascular
• Contain nerves and sensory receptors
• Located deep to the epidermis
• Has two layers:
– Papillary layer provides nutrients, O2 etc to the epidermis
– Reticular layer-interwoven network of collagen fibers
surrounding dermal organs

soleus
accessory structures
• Hair, nails, & glands in the skin (dermis)
• Hair grows everywhere except areas with thick skin and portions of
the external genitalia
• Hair is formed in organs called follicles
• Hair give added sensory info and protects orifices of the body
(nostrils, ears)

sternocleidomastoid

zygomaticus major

quadratus lumborum

subscapularis

tendinous inscriptions

simple columnar

coracobrachialis

cross sec. muscle
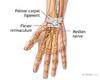
palmar carpal ligament

simple squamous

iliacus
connective tissue
• Epimysium-surrounds the entire muscle
• Perimysium-surrounds fascicles
• Fasicle-a bundle of muscle cells
•Endomysium-surrounds individual muscle cells
• Epimmysium & perimysium are attachment sites for nerves & blood
vessels

gracilis
hair
- Types of hairs on the body:
- Vellus hairs-“peach fuzz” over most of the body
- Intermediate hairs-hairs growth stimulated by hormones
- Terminal hairs-hairs on head, eyebrows, eyelashes
- Hair is dead keratinized epithelial cells