Test 1- Wk 1 Flashcards
(20 cards)
What are the three major functions of the larynx?
-control breathing/airflow -airway protection -voice production (arguably least important)
What are the three laryngeal elements?
Cartilages, muscles, vocal folds!
Where and what is the hyoid bone?
Bone above the larynx, HONORARY larynx member

Where and what is the epiglottis?
Involved with swallowing

Where and what is the thyroid cartilage?
Framework of larynx that forms thyroid notch (90 degree for men, 120 for women); superior and inferior horns form attachment points to the thyroid for muscles
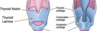
Where and what is the cricoid cartilage?
Signet ring shaped cartilage that is seen better from the back

Where and what are the cuneiform cartilages (2)?
Embedded in aryepiglottic folds and part of support not function

Where and what are the arytenoid cartilages (2)? What do they serve as attachment points for?
Very important for vocal production and breathing; rotate to abduct and adduct vocal folds. Pyramidal in shape with the apex at the top. Serves as attachment point for posterior cricoarytenoid muscle, lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, interarytenoid muscle, and true vocal fold.

Where and what are the corniculate cartilages?
On top of arytenoids and part of support not function

What is the cricoarytenoid joint? What is it’s function?
Saddle joint that allows for rocking and gliding action of arytenoids; changes length, mass, and tension of true vocal folds

What is the cricothyroid joint? What is it’s function?
Paired joints that allow for gliding action of cartilages to affect pitch

What is a voice disorder? Where are they most prevalent?
Characterized by the abnormal production and/or absence of vocal quality, pitch, loudness, resonance or duration, which is inappropriate for an individual’s age and sex- most prevalent in elderly, females, and those working with voice (teaxher, singer, manufacterer)
Why do more boys have voice d/o’s in childhood than girls?
Play loudly, with emphasis!
What is phonotrauma?
Trauma to larynx caused by vocal usage; someties overuse or misuse
What are some examples of unclear/multiple etiologies?
Screaming, sickness, tension, stress, reflux…
What are the 5 common etiologies?
Upper repiratory infection
Phonotrauma
Surgical
Illness/disease
Psychological stress
What are the categories of voice disorders?
Structural- changes in vocal folds due to injury, trauma
Functional- nothing on vocal folds
Neurological- Nerve impairment
Idiopathic- Unknown
Who is on a voice team at a medical center?
Otolaryngologist, SLP, scientist, ENT, larynogologist (oto with a specialized fellowship in d/o of larynx), GI doc, allergist, pulmonologist…
Define symptom, sign, etiology
Symptom- complaint; patient’s description of a problem
Sign- characteristics that can be observed or tested and are more objective
Etiology- Science or doctrine of causation or the demonstration of causes
What are some major symptoms of voice problems?
Rough, raspy, breathy, reduced pitch range, breaks, strain, tremor, pain, aphonia, strangled
We don’t say hoarseness… vague


