test 1 deck 4 Flashcards
pt presents post partum/c-section/nasal packing/op/tampon/diaphragm w/ diffuse scarlitinaform rash that looks like sunburn. She is complaining of vaginal tenderness. She has conjuctiva injection, strawberry tongue and desquamation of palms and soles. She has a fever >102, hypotension s<90, and signs of cardiac/hepatic, GI, GU involement. DX__ trx__

dx. Toxic shock syndrome, beta lactamase resistant (oxacillin, nafcillin, cefoxitin, vanc), I&D abscesses, remove tampon, increase hydration, vasopressors for BP
what are the two forms of erythema multiforme and what causes each?
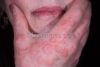
typical- herpes, URI, mycoplasma pneumoniae
atypical-medication (allopurinol, dilantin)
In newborns this is called ritter’s diseae. The child presents w/ sandpaper like scarlatinaform rash, that’s very tender, unlike scarlet fever. The child has clown facies (crusting around mouth). A skin culture is performed, but is negative for staph. You know that this is most likely caused by coagulase + staph. a. toxin that can’t be cleared by a child’s immature kidneys. dx___ tx__ locations for + cultures___
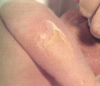
staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome, anti staph meds (diclox/cephalexin), avoid touching skin
what drugs are MC cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis?

abx -> anticonvulsants -> NSAIDS (sulfa/aminopcn’s, phenytoin/phenobarbital/valproidacid, corticosteroids/allopurinol)
treatment for drug eruption?
stop med, antihistamines, steroids III-V (careful on penis), alert for SOB
treatment for angioedema?
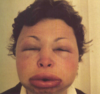
antihistamines IM, po steroids, epi ready
localized dramatic rapid swelling of sub q tissue (superficial dermis in urticaria)?

angio edema
what are the hypersensitivity syndromes?
- Erythema multiforme
- Steves-Johnson Syndrome
- Toxic Epidermal necrolysis
- erythema nodosum
- sweet’s syndrome (acute febrile neurtophilic dermatosis)
single or multiple, round, sharply demarcated, dusky red papule

fixed drug eruption
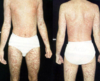
drug eruption maculopapular
MC cause of death in TEN?
infection
very sick child w/ pain presents w/ hx of rash that began on trunk then went to neck face and proximal upper extremities. The patient states they are currently taking seizure medications. the reash was preceded w/ a high fever and malaise. The patient also has lesions onconjunctiva, nasal,oraland genital surfaces that began as bullae then ulcerated andcrusted. dx__ tx__
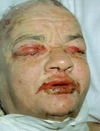
SJS, IV fluids, burn unit, ophthalmology consult, abx, NG tube
patient presents w/ itchy, uncomfortable w/ transient rash w/ orange peel appearnace and central clearing. They have SOB, difficulty swallowing, itching of mouth and throat. You know this is caused by realse of histamine from mast cell. The patient exhibits, dermatographism, and it’s brough on by exercise usually lasting 30-60 min. dx__, trx__

urticaria, acute <6 wks: IM or PO benadryl, po steroids and epi for anaphylaxis, chronic >6 weeks, antihistamine, H2 blocker, po steroids, restricitve diet, physical: avoidsnace, self limiting, H pylori testing

erythema multiforme
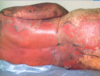
patient presents w/ mucous membrane blistering and erosion then sloughing of skin/ desquamation. The patient said it started out looking like a sunbrun that was diffuse and hot and w/in hours became painful. With slight pressure the skin wrinkles, and slides laterally (___ sign). DX__ Trx__ what organs can be effected__

toxic epidermal necrolysis, BURN unit (no corticosteroids), cyclosporine/cyclophophamide/plasma exchange, lungs(resp tract), eyes, kidneys
what are the phases of Kawasaki’s (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome) and how are they characterized?

- acute: fever, strawberry tongue, edema (palms & feet),
- subacute: end of fever-25 days, desquamation fingers and toes
- convalescent: clinical signs disappear thru norm ESR (6-8 wks)
patient presents w/ target lesion, vesicles/ bullae on their palms/soles, back of hands and mucous membranes. The patient has complaints of fever, malaise and buring lesions. They have a hx of herpes/URI/mycoplasma pneumonia. DX__ Tx___

erythema multiforme, symptomatic treatment. can give prednisone taper/ acyclovir for herpes
what is the MC site for a fixed drug reaction although they can develop anywhere?

glans penis
MC systemic vasculitis in children?
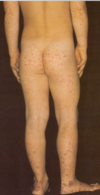
henoch-schonlein purpura
How to differentiate TEN from SSSS?

Ten seperates at the dermoepidermal junction, but SSSS splits near the skin surface (granular layer).
what is the MC small vessel necrotizing vasculitis?

leukocytoclastic (hypersensitivity) vasculitis
pt. 7wks - 12 years presents w/ 101-104 fever. They have conjunctiva injection, hypertrophic papillae (stawberry tongue), swollen palms/soles, diaper dermatitis, cervical lymphadenopathy. Their labs show high ESR, CRP, elevated platlets (thrombocytosis), WBC >20,000. DX__ TX__

kawasaki’s (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome), high dose IVIG 10-12 hrs, asa until patient afebrile (also inhibits platelet aggregation), monitor cardio: ECG, Echo for coronary artery aneurysms
child between 10-2 presents w/ palpable purpura on legs and buttocks. the patient had a uri/strep pharyngitis 2 weeks prior. The rash had a prodroms of fever and anorexia. The patient is also complaining of arthralgia and abdomen pain. You run labs see an increased ESR, serum compliment and IgA. DX__Trx___ prognosis__

Henoch-schonlein purpura, self limiting, can give NSAIDS and PO steroids (watch for GI bleed), prognosis dependent on the renal involement
what drugs are MC associated w/ SJS?

phenytoin, phenobarbital, PCNs, sulfas
patient presents w/ hx of prodrome fever, malaise, myalgia, arthralgia followed by palpable purpura (doesn’t blanch) that appear in crops lasting 1-4 wks. the lesions itch and are painful and the ones that have healed have scarred and are hyperpigmented. They are mostly located in areas w/ increased hydrostatic pressure like they legs, and arms, then back if bed bound. You know these are caaused gy immune complex doposistion on vessel walls. DX__ Tx__ underly cause__
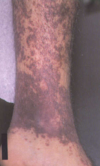
leukocytoclastic (hypersensitivity) vasculitis, stop suspected meds, treat underlying conditoin, prednisone 3-6 wks, colchicine. viral hepatitis, bacterial-strep, UTI, drugs-pcn, sulfa, SLE, malignancy
MC drug eruption?
exanthems (maculopapular)
what complications of SJS are most concerning?

sloughing of upper and lower respiratory tract, blindness due to corneal lesions


