Teach yourself properties and microstructure Flashcards
What is uniaxial loading?
Load is perpendicular to the cross-sectional area.
What is work hardening?
A specimen under loading will reach a yield point, past the yield point the load will be causing plastic deformation which is referred to as work hardening.
What is the ultimate tensile strength?
Past the yield point, the highest stress the specimen can take before failing, usually failing through a process called necking.
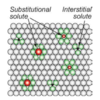
What is a interstitial solute?
What is a substitutional solute?
Only small atoms (H,C) form interstitial solid solutions: These atoms can fit into the gaps between metal atoms. (C in Fe: carbon steels)
Most solids solutions will be substitutional: atoms of similar size replace one another in the lattice.
Difference between primary and secondary bonding?
Primary is in metals, ceramics and along long-chain polymer molecules while secondary are found between polymer chains and in materials such as ice.
Primary are 100 times stronger than Secondary.
Explain the 3 different types of primary bonding.
Metallic - Bonding is by electrostatic interactions between the ions and free electrons. Bonds strong in all directions, for regular crystal lattices.
Ionic - Electrons transferred between atoms to produced attracted ions. Bond is non directional, insulators, pack into regular lattices.
Covalent - Electrons shared between atoms. Covalent bonding is directional. Insulators, have regular lattices.
Explain how primary bonding can be generally modelled, in terms of springs and draw the force separation graph for atoms.
Primary bonds can be modelled as stiff springs with a non-linear force-separation characteristic(graph).
The stress-strain graph is based of this graph, the reason the stress-strain graph is linear (until the yield point) is because the force-separation graph is linear for small separations between bonded atoms.
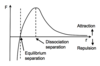
What is secondary bonding?
Secondary bonds operate at much larger atomic separation than primary bonds and are much weaker. They occur due to dipoles between molecules and atoms.
- Hydrogen bonds form the strongest dipoles, and are the commonest secondary bond between polymer chains.
- In secondary bonded materials(polymers), the bonds become ineffective at much lower thermal energy (kT) than primary, giving low melting points.
What are the main three types of metallic packing?
- Face-centered cubic(FCC)
- Close-packed hexagonal(CPH)
- Body-centered cubic(BCC)
What are close-packed crystal structures?
Basic building block for FCC and CPH. Highest density of atoms arranged in a plane is hexagonal packing. The close-packed directions are the straight lines through the centres of touching atoms.
What is a unit cell?
A unit cell is the smallest unit which can be replicated by translation in all directions to build up the 3D crystal structure. The unit cell dimensions are called the lattice constants. The unit cells are drawn with the atoms reduced in size, for clarity
- remember that they touch in close packed directions.
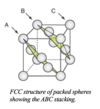
Describe a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure.
The FCC structure is described by a cubic unit cell with one atom at each corner and one at the centre of each face, the close-packed planes(ABC..) are perpendicular to the cube diagonals.
Any of the four diagonals of the cube lies normal to sets of ABC-stacked planes.
Give some characteristics that FCC metals have.
- They are very ductile when pure, work hardening rapidly but softening again when annealed, allowing them to be rolled, forged, drawn or otherwise shaped by deformation processing.
- They are tough, i.e. resistant to crack propagation.
- They retain their ductility and toughness to absolute zero, something very few other materials allow.
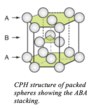
Describe the close-packed hexagonal (CPH) structure.
The close-packed planes stacked in an ABAB… sequence are easily identified:
the close-packed planes are perpendicular to the axis of the prism. There are two lattice constants in CPH - the side-length of the hexagonal base, a, and the height of the prism, c.
The first is clearly equal to the atomic diameter, as the atoms are touching; geometry gives the relationship between this and the second lattice constant.
Give some characteristics that CPH metals have.
They are reasonably ductile (at least when hot), allowing them to be forged, rolled, and drawn, but in a more limited way than FCC metals.
Their structure makes them more anisotropic than FCC metals(i.e. crystal properties vary with direction).
Describe the body-centered (BCC) structure.
The structure is not close packed
- It is made by stacking planes of atoms in a square array. Atoms touch along the cube diagonals, so these are the close-packed directions.

Give some characteristics BCC metals have.
They are ductile, particularly when hot, allowing them to be rolled, forged, drawn or otherwise shaped by deformation processing.
They are generally tough, and resistant to crack propagation at and above room temperature.
They become brittle at low temperatures. The change happens at the “ductile-brittle transition temperature”.

Explain what the atomic packing fraction is and how to calculate it.
It is the fraction of space occupied by atoms. It is calculated by calculating the number of atoms per unit cell ( corner atoms are shared between 8 cells, face atoms between 2).
Then you divide the total volume the atoms take by the volume of the unit cell.
How do you calculate the theoretical density of metal?

What is a interstitial space(or hole)? and what sort do the FCC, CPH and BCC structures have?
A space between the atoms or molecules. The FCC, CPH and BCC structures contain interstitial space of two sorts: tetrahedral and octahedral.
Name which structures have tetrahedral holes.
FCC
BCC(requires two unit cells)
Name which structures have octahedral holes.
FCC
CPH
Why does adding carbon into the interstitial holes of iron increase the carbon steels strength?
Interstitial solute atoms are particularly important for carbon steel, which is iron with carbon in some of the interstitial holes. Iron is BCC(at room temp), and only contains tetrahedral holes.
Carbon will go into these holes, but because its too big, it distorts the crystal structure. It is this distortion that gives carbon steels much their strength.
How can more carbon be added to steel?
Iron transforms to FCC( at temperatures around 800*C). This means that much more carbon will “dissolve” into FCC at high temperature than in BCC (room temp).
Describe the diamond cubic (DC) structure.
Carbon, silicon and germanium atoms have a 4-valent nature
- each atom prefers to have 4 nearest neighbours, symmetrically placed around them. If you first ignore the numbered atoms, the remainder form an FCC lattice; the atoms numbered 1-4 are then additional atoms located in half of the tetrahedral interstitial spaces.
As the tetrahedral hole is far too small to accommodate a full-sized atom, the others are pushed further apart, lowering the density.

Give uses for: Silicon, Germanium Carbon as diamond Silicon carbide
Semiconductors
Cutting and grinding tools, jewellery
Abrasives, cutting tools
Describes the Corundum structure.
A number of oxides have the formula M2O3, among them alumina, Al2O3.
The oxygen, the larger of the two ions, is close-packed in a CPH stacking.
The M atoms occupy two thirds of the octahedral holes in this lattice.
What is the name of the weak forces experienced between polymer chains?
van der Waals bonds.
Why are polymers inherently low in density?
They are made of light elements (carbon, hydrogen), and the low packing density of the molecules leaves more “free space” in the structure.
What are the names of the three main classes of polymer?
Thermoplastics, thermosets and elastomers.
In all cases the long-chain molecules pack together randomly, giving an amorphous structure.
What are thermoplastics?
Thermoplastics contain no cross-links but can be either amorphous or semi-crystalline.
Amorphous thermoplastics are arranged randomly with occasional entanglement points between chains, these restrain deformation and sliding of molecules.
Since the crystalline regions are more tightly packed than amorphous regions, this can lead to significant shrinkage on crystallization. This can lead to lower dimensional precision in manufactured polymer components.
What does the ease with which a thermoplastic crystallizes depend on?
The ease with which a thermoplastic crystallises is determined by the complexity of the side groups:
simple thermoplastics: semi-crystalline - nylon, polyethyline
complex thermoplastics: fully amorphous - perspex,polycarbonate
What are elastomers?
Elastomers contain a small number of cross-links, between simple chain molecules.
Further cross-linking can be triggered in service(by UV light) leading to polymer degradation.
What are thermosets?
Thermosets have extensive cross-links between chains.
For the FCC structure, show that the ratio of the lattice constant ( the size of the cube ) to the atomics radius is equal to 2 × 20.5.

For the CPH structure, show that the ratio of the lattice constant, c:a is equal to 1.633.

For BCC, show that the ratio of lattice constant to atomic radius is 4R / 30.5.

Calculate the atomic packing fraction value for CPH.



