Sweatman - Prostate Cancer Flashcards
What hormones are implicated in prostate cancer?First-line therapy? Alternative approaches?
- Most hormone-sensitive of all cancers
- Any hormonal therapeutic strategy must take into account the 2 almost equivalent sources of adrogens acting in the prostate
1. Testosterone produced by testicles
2. Locally produced DHT derived from dehydroepiandrosterone from adrenals - FIRST-LINE: combined androgen blockade -> med or surgical castration + pure anti-androgen
1. Non-drug approaches: watchful waiting or active surveillance, & external beam radiation
2. Implanted I125 titanium coated “seeds” used to tx early stage disease -> brachytherapy
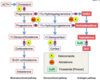
Briefly describe the HPA-T axis, and its available drug targets for prostate cancer tx.
- CRH + GnRH from hypothalamus -> ACTH + LH from anterior pituitary -> adrenals + testes
-
GnRH agonist/antagonists and CYP17A1 INH can block DHEAS, DHT, and testosterone production, alleviating their proliferative signals on the prostatic cancer androgen receptor
1. Note: not included in this diagram is that CYP17A1 antagonists act in the prostate tissue itself as well - Androgen receptor antagonists can be used to bind to and block androgen signaling on the tumor cell itself

How might a prostatic tumor evade hormone therapy? Describe 2 specific mechanisms for this change.
- Like other hormonally responsive tumors (i.e., breast cancer), a prostatic tumor can evolve into an androgen-insensitive growth pattern
1. AR continues to be expressed, and signaling remains intact - Androgen-independence is derived from changes in AR amplification, by point mutation, & changes in expression of AR co-regulatory proteins -> “super AR” that can respond to lower concentrations of androgens or the ability to function in a ligand-independent manner
- Alternatively, there can be a gain of stability mut in 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, the enzyme that that governs the conversion of DHEAS to DHT; normally this is a minor conversion to a more potent androgen, but INC capacity can lead to DHT mediated tumor activation
How does GnRH agonist treatment affect prostatic tumors? Drugs?
- Normal GnRh release pulsatile, but agonist tx is continuous -> down-regulation of GnRH receptor in ant pit, leading to DEC LH and FSH
1. Serum levels of T fall to castrate levels in 2-4 weeks - Can avoid initial transient disease flare by 2-4 wks of AR blockers
- DRUGS: Goserelin, Histrelin, Leuprolide, and Triptorelin

What are the AE’s of the GnRH agonists (table)?
- AE’s consistent with hypoandrogenic state: occurs over a short period of time (2-4 weeks)
- DEC in bone mineral density caused by low estogen levels
- Elevated serum lipids, weight gain, and DM INC the risk of CV disease
- Sexual dysfunction, gynecomastia, loss of libido
- All are capable of producing injection site reactions upon administration (all SC or IM)

Degarelix MOA and AE’s
- Reversible GnRH receptor antagonist (SC): DEC LH, FSH secretion -> castrate testosterone levels in 3 days
- COMMON AE’s: hot sweats, injection site reaction, weight gain
1. HTN, arthralgia, chills, fatigue, impotence
2. Elevated hepatic enzymes (reversible), and QT prolongation - NO initial disease flare
Estramustine MOA and AE’s
-
Binds EMBP on prostate CA: INH microtubules, promoting disassembly and G2/M arrest -> DNA strand breakage (alkylating agent attached to estradiol structure; see attached image)
1. T levels depressed: (-) feedback on HP axis -
Oral; comparable estrogenic effects to estradiol
1. Edema, thromboembolism, MI, PE, and stroke possible - COMMON AE’s: GI upset, gynecomastia, mastalgia (breast pain), and impotence
1. Elevated hepatic enzymes and hyper-bilirubinemia also reported

What are the sites of action, CYP activity, and AE’s of the androgen receptor blockers?
- Flutamide is the only one used for women’s health mgmt: tx of hirsutism or PCOS -> teratogen
1. Enzalutimide: male-mediated teratogenicity - AE’s: consistent with hypo-androgenic state, even though androgen levels NOT depressed
1. Enzalutamide: CNS effects, incl. seizures
2. BBW’s: hepatotoxicity w/Flutamide and resp insufficiency with Nilutamide - NOTE: Bicalutamide is the only with CYP activity, and that is also a partial agonist
1. Flutamide is the only one that does NOT act centrally

Sipuleucel-T MOA and AE’s
- MOA: autologous cellular immunotherapy to stimulate T-cell immunity against prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)
1. Pt APC’s (leukapheresis) cultured with recombinant PAP-GM-CSF -> take up Ag, process and express fragments on surface
2. Product (w/T, B, NK-cells) reinfused -> can prime CD8+ T-cells to kill the cancer - AE’s: mild infusion rxns, fever, chills, dyspnea, GI effects like N/V
1. Paresthesias, citrate toxicity, fatigue

How do CYP17A1 (17-alpha hydroxylase) INH work?
- CYP17A1 mediates conversion of pregnenelone or progesterone to androgens -> INH of this enzyme DEC androgen levels, resulting in prostatic tumor losing its proliferative signal
- Produces a HYPER-mineralocorticoid state (unlike Ketoconazole, which does the opposite) b/c it prevents transition of products from this pathway into the other parallel pathways, providing more substrate for later sequential reactions
Abiraterone MOA and AE’s
- CYP17 INH
- Produces INC mineralocorticoid state: HTN, hypo-kalemia, fluid retention (*caution w/pre-existing CV issues)
1. Symptoms prevented/DEC w/corticosteroids to suppress ACTH drive; adrenocortical insufficiency if withdrawn too quickly - Elevated hepatic enzymes; routine LFT’s required
- Cat X drug; precautions necessary for F partner (she should not handle the drug; wear condoms)
Appreciate this.

Good job!
What hormones are important for maintenance of male bone health?
Estrogen and testosterone (and obviously, Vit D and PTH too)

Estrogen patch MOA, AE’s
- Feedback INH of LHRH and LH, DEC androgens to castrate levels
- Bone protective: bone loss w/other androgen-depriving drugs via loss of aromatized estrogen
- Not used orally bc high dose can produce significant CV AE’s: DVT, thromboembolism, and Na+/H2O retention
Should Finasteride and Dutasteride be used for prostate cancer chemoprevention?
- No good evidence; drug benefit is questionable
- May be used off label; prevent conversion to the more active form of T, DHT
- FDA says this use does NOT have a favorable risk-benefit profile
1. New paper notes the pharmacologic impact of these drugs independent of their 5-alpha reductase INH, but still more work to be done to prove an effect/benefit
How is ER-alpha implicated in prostate CA?
- Expressed in both the epithelium and stroma
- ER-alpha mediates abberant proliferation, inflam, and malignancy
- Induction of inflam by ER-alpha may also promote malignancy, and stimulate aromatase expression, which is altered in malignancy and may be driven by inflammatory cytokines, stimulating a cycle of activity

How are progesterone receptors implicated in prostate CA?
- Inducible by estrogen, and found in more than half of primary prostatic cancers
- Consistently expressed in androgen-insensitive tumors
How is ER-beta involved in prostate cancer?
- Glandular epithelium
- ER-beta exerts a number of beneficial (and protective) anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects -> TUMOR SUPPRESSIVE EFFECT
- Anti-inflammatory effects may also result in DEC aromatase expression, and reduced local estrogens
- May even lead to initiation of apoptosis in TNF-alpha dependent manner
- High affinity for phytoestrogens: genistein and other soy isoflavones

What conventional chemo is approved for prostate cancer tx?
- Docetaxel and Carbazitaxel are approved for metastatic prostate cancer
1. Premedication w/corticosteroids +/- anti-H1 and H2 histamine blockers to preempt edema and injection rxns produced by these surfactant-containing drug preps - Mitoxantrone + Prednisone used for palliation of severe pain from advanced hormone-refractory disease
Carbazitaxel
- Unlike other taxanes, it is a poor substrate for the multidrug resistance P- glycoprotein efflux pump and may be useful for treating multidrug-resistant tumors
- Penetrates the BBB, where Pgp efflux pumps may serve as barriers


