Phillips - Menopause Flashcards
1
Q
What is menopause?
A
- 1 year without menses and FSH >30 (because estrogen goes down)
- NOTE: women now spend about 40% of their lives in menopause, which begins around ag 45-55

2
Q
What is perimenopause?
A
- Age group near menopausal age, 45-55
- With symptoms: menopausal transition
3
Q
What is post-menopause age group?
A
- Postmenopause: beyond menopause, or age >55
4
Q
What is the biology of menopause?
A
- End of reproductive life about age 43
- Ovary continues to produce eggs sporadically, but they are abnormal
- With ovulation, estrogen still being produced, but in lower amounts (no progesterone)
1. With less amounts of estrogen being produced, FSH rises
2. Menses becomes less frequent, lighter - Menopause defined as:
1. No menses for a year
2. FSH >30 (bc estrogen levels go down)
5
Q
What things bring women to the OB to begin hormone therapy (bar chart)?
A

6
Q
What are the symptoms of menopause?
A
- Most common: hot flashes -> skin changes and vasodilation have been documented
- May report waking up at night with sweats, then cooling effect -> may happen 5x/night, and disturb sleep
1. If no treatment, will dissipate - Vaginal atrophy (can cause dyspareunia): late effect, but can tx w/estrogen, vaginal or systemic
- Probably due to gonadotropin spikes as much as estrogen deficiency
- May occur as peri-menopausal symptoms
7
Q
What are the FDA-approved indications for HRT?
A
- Indicated for:
1. Treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause -> 1o indication, and most common reason women start therapy
2. Treatment of vulvar and vaginal atrophy: topical vaginal products should be considered
3. Prevention of postmeno osteoporosis: FDA encourages consideration of non-estrogen meds when HT is prescribed solely for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
8
Q
What are the options for post-meno HRT?
A
-
Estrogen: can be taken alone only by women who have had a hysterectomy
1. Estradiol pill, transdermal patch, or gel
2. Conjugated estrogens: Premarin -
Progestin added: for pts that have a uterus, to prevent endometrial hyperplasia and cancer:
1. Medroxyprogesterone
2. Micronized progesterone
9
Q
What symptoms are erroneously associated with menopause?
A
- Depression
- Lack of interest in sex
- Going crazy
10
Q
How should post-meno women with vaginal complaints only be treated?
A
- Examples: dryness, dyspareunia
- Preferred tx is low-dose, vaginal estrogen; FDA-approved use
- NO need for progestins
11
Q
What 3 medical illnesses are associated with menopause?
A
- Osteoporosis
- Heart disease
- Cancer
12
Q
Can estrogens be used to treat osteoporosis?
A
- NO -> only used to prevent osteoporosis
1. Individual risk factors
2. Screening via BMD msmts starting at 65-y/o
3. Should have another indication for HRT
4. Affects osteoclast and osteoblast activity: even low-dose estrogen therapy can INC BMD - Tx is bisphosphonates
13
Q
Who is at high-risk for osteoporosis?
A
- High-risk groups:
1. Caucasian/Asian
2. Thin
3. Smoker, alcohol Use
4. Steroid Use
5. Family History
14
Q
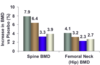
Describe the effects of combo and estrogen HRT on fracture risk.
A
- Significant reduction in hip, vertebral, and all fractures in Women’s Health Initiative study
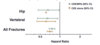
15
Q
How does estrogen affect CV risk?
A
- Women protected from CVD until menopause (when compared to men)
- Early loss of endogenous estrogen (via oophorectomy or premature ovarian failure, for example) is associated with CVD
- Endogenous estrogen INC smooth muscle proliferation, lowers cholesterol, and improves vascular tone
- Remember: also associated with VTE, PE


