Surgery MSK Flashcards
What is Becker’s Muscular Dystrophy vs Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Beckers = Insufficient dystrophin due to gene mutation Duchenne = no dystrophin
Inheritance pattern of Beckers muscular dystrophy
X-linked
Axial traction on elbow causes?
Nursemaids elbow
how to tx nursemaids elbow
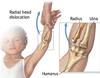
hyperpronation or….
supination plus flexion
Tennis Elbow
Lateral Epicondylitis with repetitive contraction of extensor muscles
Golfer Elbow
Medial Epicondylitis - tenderness over medial epicondyle with wrist flexion
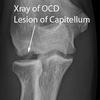
Panner disease
Osteochondrosis of capitellum
unclers from venous insufficiency occur where
medial malleolus
medial malleolus ulcers caused by what
venous insufficiency (venous valve incompetence)
What causes diabetic foot ulcers
- peripheral neuropathy
- microvascular insufficiency
- immunosuppression
Pain between 3rd and 4th toes
Morton Neuroma
Hypermetabolic phase (post burn phase )
increases in catecholamines and cortisol
because muscle degradation is used for metabolism
associated with elevated Cardiac Output
Planta fasciitis
burning pain on plantar side of foot. Pain decreases with activity. Common with runners
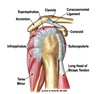
MC rotator cuff injured muscle
supraspinatus
Rotator Cuff Muscles
SITS:
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
Fall on outstretched hand may tear what
What about Fall on outstretched hand in old lady
What about Fall on outstretched hand in young kid
rotator cuff
old lady = Colle’s fracture (distal radius displaced)
young kid = scaphoid fracture

winged scapula
Long thoracic nerve cut to serratus anterior muscle
what is drop arm test
may detect rotator cuff tear

Popeye sign
weakness with supination with intact forearm flexion denotes
long head of biceps rupture

Klumpkes Palsy
from sudden upward pulling on the arm
usually ulnar nerve
weakness and atrophy of hypothenar and interosseous muscles
“claw hand deformity”