Strep Flashcards
(51 cards)
strep pyrogenes
pharyngitis and skin/soft tissue infections
viridans strept
infective endocarditis
strep pneumoniae
pneumonia, upper rest tract infect & meningitis
enterococcus faecalis & enterococcus faecium
nosocomial infections
distinguishing test between staph and strep
catalase test
strep is negative
strep gran stain and culture
gram + cocci
spherical
chains or pairs
which bacteria is Beta hemolytic?
streptococcus pyogenes
streptococcus pneumonia: hemolysis, solubility in bile, optochin resistance?
alpha
bile soluble
inhibited by optochin
viridans strep
“green strep”
alpha
not bile soluble
not inhibited by optochin
Group A:
strepto pyrogens (sensitive to bacitracin)
Group B:
streptococcus agalactiae (resistant to bacitracin, hydrolyzes hippurate)
Group D:
hydrolyzes esculin in presence of bile- produces black pigment
- enterococcus: grows in nacl
- strep bovis: no growth in nacl
What is the most important virulance factors in strep pyogens?
- M protein: inhibits opsonization: block phago
antibody M strain specific immunity
- capsule: antiphagocytic
antibodies not made against capsule bc made of HA (found in body)
Strep enzymes:
streptokinase: activates plasminogen to form plasmin (dissolves fibrin clots)
streptolysin O: anti (ASO) AB used as marker of recent group A strep infection
* high ASO useful for dignosing rheumatic fever
Strep toxins:
erythrogenic toxin: causes rash of scarlet fever
-superantigen ( T cell divide and produce cytokines)
Toxins involved in clinical presentation of Strep pyogenes.
Toxic shock syndrome: exotoxin A (superantigen)
*similar to staph (but strep has site of soft tissue infectoin & +culture)
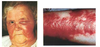
necrotizing fascitis- exotoxin B
where is streptococcus pyogenes normally found
skin, oropharynx
What are the three types of diseases it causes?
- pyogenic
- toxigenic
- immunilogic
explain the pyogenic (Strep pyrogenes) disease
inflammatio induced locally at site whre orgasm are present
- pharyngitis
- cellulitis
explain the toxigenic (Strep pyrogenes) disease
exotoxin production can cause systemic symptoms at sites where not organism is found
- scarlet fever
- toxic shock syndrome
explain the immunologic (Strep pyrogenes) disease
causes inflammation at site where no ogms (sequelae)
- rheumatic fever
- acture glomerulonephritis
Strep throat

strep pyogenes
pharyngitis
main disease in children and adolescents
fever, sore throat w/ tonsillopharyngeal erythemia and exudates, tender cerival LN
elevated WBC
strep throat detection test and treatment
- throat swab for antigen detection test or culture
- distinguish infect vs normal flora - usually recover spontaneously
- may prevent rheumatic fever - can extennd to cause pharyngeal abscess, otitis, sinusitis, mastoiditis, meningitis
strep pyogenes: skin and soft tissue infections