Staphylococci Flashcards
staphylococci characteristics
gram +, clusters
single cell membrane, thick cell wall
non-motile, non-sporeforming, facultative anaerobe
polysac capsule differs among strains
catalase positive
Staph aureus
catalase +
coagulase + (prothrombin to thrombin–>fibrinogen to fibrin–>clot)
beta-hemo, golden colonies
normal flora of staph aureus
anterior nares; also vaginal, perirectal, inguinal areas
enter by beaks in skin, trauma, insect bites, catheters, etc
What does this picture show?

pyrogenic disease–> cellulitis of skin with our without absecess (point to area of least resistance)
What are other pyrogenic skin manifistation?
impetigo, folliculitis, furuncle, carbuncle
Enterotoxin
pre-formed by bacteria in food before ingestion–>food poisoning
TSST-1 produced locally (eg. cellulitis or vaginal tampon)–>blood systemic effects
If staph aureus becomes bacteremic what can it cause?
endocarditis, osteomyelitis
What is the mechanism of suprantigens?
cross link T cells R and class II MHC molecules–> stimulate T cells non specifically–> release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFa)–>shock
What caused this?
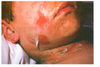
toxic shcok syndrome- may occurs with localized infection such as cellulities or with vaginal tampon or post surgical packing
manifistations- fever, erythema of the skin, followed by desquamation, conjuctivitis, strawberry, delirium, and shock
What bacteria causes this?

staph aureus–>scalded-skin syndrome
infants/young children
fever and generalize desquamation with large bullae
exfoliant, a protease, caues separation of layers in the spidermins
virulance factors: adhesion to host cells and substances:
teichoic acids- polymers of ribitol phosphate and lalow bacterial to stick to mucosal cells
lipoteochoic acid- pro-inflammatory
virulance factors: enzymes
coagulase- clots that walls off abscss from leukocytes
staphylokinase- plasminogen activator, lyses fibrin, allow spread of infection
virulance factor: PV-leucocidin-
post forming tocin that damages WBC, associated w/ severe skin/soft tissue infect and MRSA
virulance factor: avoidance of host responses
proteins A binds to Fc fragment of IgG at site that complement binds, thereby preventing activation of complement
virulance factors: carb capsule
poorly immunogenic
Treatment for suppurative infections?
incision and surgical drainage may be enough, AB alone not enough
tx for TSS- remove foreign body or drain the suppuration. support BP and cardiac fxn
Diagnosis for s. aureus
gram stain smears show gram + cocci in clusters, but absence does not rule out!
in TSS- profound systemic effects, but blood cultures are often negative
no antigen, toxin, or ab test
What does a positive blood culture for S. epidermidis tell us?
may be from contamination at phlebotomy site
s. epidermidis characteristics
coagulase -
novobiocin sensitive
infect acquire through hospital or invasive med procedure, catheters, artificial heat valves, foreign body, etc.
lack toxins and invasion enzymes, no TSS
Biofilms
bacteria attached to foregn body express exopolysaccharide
will help bacteria avoid immune defenses (eg. phagocytosis)
Biofilms also occur w/ S. aureus
antibiotic resistance
penicillin–>methicillin/nafcillin/cephalosporins–>vancomysin–>daptomycin/quinupristin-daldopristin
MRSA
90% strains have plasmid that encode a beta-actamase enzyme–>thus penicillin resistant
>50% of hospital strains and increased number of community acquired strains carry transferable mecA genes that encode altered penicillin-binding proteins–>met resistant (also to nafcillin, oxacillin, and cephalosporins
- may be resistance to fluroqinolones, and topical muprocin
- vanco resistant too, but less frequent.


