Stats_Exam 2 Flashcards
(25 cards)
Define a random experiment
an action whose outcome cannot be predicted with certainity. Each subject equally likely.
Define a sample space
the collection of all possible outcomes for an experiment
Define an Event
a collection of outcomes. A subset of a sample space.
Define mutually exclusive
2 or more events, no 2 having anything in common
Define independent events
may still have something in common, but does not affect the probability of the former event.
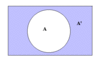
Define the complement of an event
1- the probability the evend does not occur. Not A
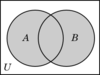
Descrime the union of 2 events
A can occur B can occur or Both can occur
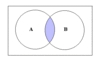
What is the intersection of 2 events
A and B occur simultaneously
P(A) = 1 means..
the event is certain to happen
P(A) = 0 neabs
the event will NOT happen
What rule does this equation fall under:
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
Special Addition for mutually exclusive events
The complementation rule formula
P(A) = 1 - P(not A)
What rule does this equation fall under:
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A + B)
General Addition Rule. Because it will always get you the right answer
What is a contingency table?
- the distribution of one variable in rows another in columns
- study the association between the two variables
the probability of one event occuring when it’s known that another one has occurred.
Conditional Probability
Finish the equation P ( B | A)=
P(A & B) / P(A). (Pay attention to the sample size.) General Conditional Rule.
When referring to the intersection of 2 events, What is the general rule?
P(A & B) = P(A) * P (B | A)
What is the special conditional rule-
When A & B are independent events. P(B | A) = P(B)
When referring to the union of 2 events. What is the special rule for independent events
P( A & B) = P(B) * P(A)
What is a random variable?
a numerical value that’s determined by chance
Define the probability distribution
the probabilities with which X takes those values
How to remember greater than and less than….
the pointy end is facing the smaller one ex 9 >6
When reading the equation, decide which formula to use before you plug in the equation
If two events are mutually exclusive, what is their probability?
0


