Sports Science Quiz - Level Hard Flashcards
This class was not made by Teacher Bló but taken from a Sports Science Teacher and adapted by Teacher Bló
1.2.2
Distinguish between the different types of muscle

1.2.1
What are the characteristics of Muscle?
Excitability is the ability to respond to a stimulus, which may be delivered from a motor neuron or hormone
Contractility is the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten
Extensibility - they can be stretched.
Elasticity - they return to normal length after stretching.
1.2.4
Define the terms origin and insertion of muscles.
- The origin is where the tendon of the muscle joins the stationary bone(s). Usually more proximal.
- The insertion is where the tendon of the muscle joins the moving bone(s). Usually more distal.
1.2.3
Annotate the structure of skeletal muscle.

Name the muscle (yellow), the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
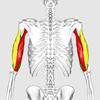
Triceps Brachii
Movement. Elbow extension (agonist)
Elbow flexion (antagonist)
Origin: Scapula/ Humerus
Insertion: Ulna
Name the muscle below, and the joint movement it is responsible for.
Include its origin and insertion.
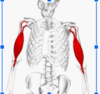
Bicep Brachii
Movement: Elbow flexion. (agonist)
Elbow extension (antagionsit)
Origin: Scapular
Insertion: Radius and Ulna

Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
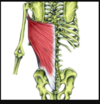
Latissimus Dorsi
Joint: Shoulder
Movement: Adduction, extension. (agonist)
Abduction, flexion (antagonist)
Origin. Thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: Humerus.
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
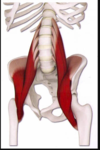
iliopsoas
Movement.
Hip flexion (agonist)
Hip extension (antagonist)
Origin. Lumbar vertebrae
Insertion. Femur.
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
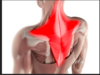
Trapezius
Movement: Shoulder elevation (agonist)
Shoulder depression (antagonist)
Origin. the base of the skull (cervical vertebrae)
Insertion: Clavicle & scapula.
Name the 4 muscles that make up the quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris is a hip flexor and a knee extensor. It consists of four individual muscles; three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris.
It is located in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
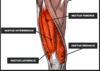
Name the 3 muscles of the hamstrings.
The three major muscles of the hamstrings are the:
biceps femoris
semimembranosus
semitendinosus
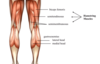
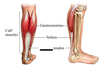
Name the muscles on the posterior aspect of the lower leg.
(from the knee down)
Gastrocnemius
Soleus (underneath the gastrocnemius)
Achilles tendon
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
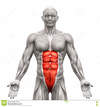
Rectus Abdominis
Movement: Flexion of the spine
Origin: Pubis
Insertion: Sternum
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.

External Obliques
Movement: Lateral trunk flexion
Origin: lower Ribs
Insertion: Ilium
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.

Erector Spinae
Movement: Trunk extension
Origin: Thoracic Vertebrae, ilium
Insertion: Ribs and Thoracic vertebrae, Sacral vertebrae
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
(3 parts)

Deltoids
Red = Anterior
Green = Middle / lateral
Blue = Posterior
Movement: Extension, Flexion, and abduction of the shoulder
Origin: Clavicle, Scapula
Insertion: Humerus
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.

Pectoralis Major
Movement: Flexion and Abduction of the shoulder
Origin: Sternum, clavicle
Insertion: Humerus
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
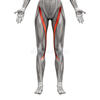
Sartorius
Movement: Hip flexion, Hip abduction, Knee flexion
Origin: Ilium
Insertion: Tibia
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
(4 different Parts)

Quadriceps
Blue = Rectus femoris (RF)
Green = Vastus intermedialis (VI)
Yellow = Vastus lateralis (VL)
Red = Vastus medialis (VM)
Movement: Knee Extension, Hip flexion (RF)
Origin: Ilium (RF), Femur (VI, VL, VM)
Insertion: Patella and Tibia
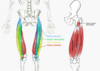
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.

Hamstrings
Green = Semitendinosus (ST)
Yellow = Bicep Femoris (BF)
Purple = Semimembranuses (SM)
Movement: Hip extension, Knee flexion
Origin: Ischium (below Sacral Verterbrae)
Insertion: Medial Tibula, Lateral Tibula/ Fibula

Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
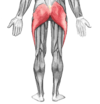
Gluteus Maximus
Movement: Hip extension
Origin: Coccyx Vertebrae, Ilium, Sacral
Insertion: Femur
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.

Tibialis Anterior
Movement: Dorsiflexion of the foot
Origin: Tibia
Insertion: Tarsals/ Metatarsals of foot
Name the muscle, the joint it moves, and its origin and insertion.
(two different Muscles)
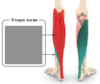
Gastrocnemius and Soleus
Red = Gastrocnemius (GN)
Green = Soleus (S)
Movement: Plantarflexion of foot
Origin: Femur (GN), Tibula / Fibula (S)
Insertion: Both (GN and S) from Achilles tendon which attaches to heel and foot

Describe the difference between tendons and ligaments.
Tendons connect muscle to bone.
Tendons are a part of the muscle, they are the very end part of each muscle, and is the structure which attaches the muscle to the bone.
They share characteristics of muscles (like elasticity) but are not as elastic as the belly of the muscle. (for example)
Ligaments attach bone to bone.
They do not share the characteristics of muscles like elasticity, and contractility. They are stronger than tendons and provide for structural support for joints, than tendons.

What are the 5 main functions of the skeleton?
Support,
Movement,
Protection,
Mineral and Fat Storage,
Blood Cell Formation
https://open.oregonstate.education/aandp/chapter/6-1-the-functions-of-the-skeletal-system/
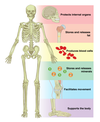
Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton.
The Axial Skeleton (grey)
The axial skeleton forms the vertical, central axis of the body and includes all bones of the head, neck, chest, and back
The Appendicular Skeleton (blue)
The appendicular skeleton includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs, plus the bones of the pectoral and pelvic girdles that attach each limb to the axial skeleton.
https://open.oregonstate.education/aandp/chapter/7-1-divisions-of-the-skeletal-system/
Name 4 long bones.
Femur
Humerus
Tibia
Fibula
Metacarpals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges.
The femur is _______ to the patella?
Proximal
The radius is _________ to the ulna.
Lateral
The mandible is ________ to the cranium.
Inferior


