SPINAL CORD Flashcards
SPINAL CORD
anatomy
(boundaries + gross anatomy)
starts: medulla below the pyramidal decussation
terminates: conus medullaris (L2)
fissures + sulcus

SPINAL CORD
anatomy
(gray and white matter)
GRAY MATTER
centrally located
butterfly
cell bodies + dendrites + proximal part of axon
WHITE MATTER
surrounds gray matter
tracts or fasciculli
axons

SPINAL CORD
components of gray matter
dorsal horn (sensory)
ventral horn (motor)
intermediate zone (autonomic)
T1 - L2 + S2 - S4
Clarke’s nucleus (T1 - L2)
SPINAL CORD
components of white matter
tracts and fasciculli
SPINAL CORD
spinal nerves
(31 roots)
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
SPINAL CORD
typical root
(spinal nerve)
ventral (motor) and dorsal (sensory) roots
dorsal root ganglion (sensory)
ventral and dorsal ramus (mixed)

SPINAL CORD
plexus
brachial: C5 - T1
(upper limbs)
lumbarsacral: L2 - S3
(lower limbs)
cervical + lumbar enlargement in spinal cord
SPINAL CORD
cauda equina
dorsal + ventral roots of
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
SPINAL CORD
conus medullaris
caudal end of spinal cord
S3 - S5
adults: L2 vertebra
SPINAL CORD
filum terminale
slender pial extension
tethers the spinal cord to the bottom of the vertebral column
SPINAL CORD
types of nerve fibers
(Erlanger-Gasser)
Group A
heavily myelinated
Group B
moderataly myelinated
Group C
unmyelinated
SPINAL CORD
Group A nerve fiber
150 m/s
somatic fibers (sensory + motor)
subdivision
alpha
beta
gamma
delta
SPINAL CORD
Group B nerve fiber
15 m/s
sensory and motor autonomic fibers
sensory - general visceral afferent
motor - preganglionic
SPINAL CORD
Group C nerve fiber
no more than 2 m/s
sensory + motor fibers
sensory - pain + temp
motor - posganglionic (autonomic)
SPINAL CORD
other classification of fibers
(functional division)
motor fiber
(alfa, beta and gamma)
sensory fiber
(Ia, Ib, II, III and IV)
autonomic
(pre and postganglionic)

SPINAL CORD
motor fibers
alpha
A-alpha (Erlanger-Gasser)
extrafusal muscle fibers
beta
A-beta (Erlanger-Gasser)
gamma
A-gamma (Erlanger-Gasser)
intrafusal muscle fibers

SPINAL CORD
sensory fibers
Ia
A-alpha (Erlanger-Gasser)
muscle spindle (primary or annulospiral ending)
Ib
A-alpha (Erlanger-Gasser)
golgi tendon
II
A-beta (Erlinger-Gasser)
muscle spindle (flower-spray ending) + cutaneous mechanoreceptors
III
A-delta (Erlinger-Gasser)
free nerve ending (touch and pressure)
nociceptor (sharp pain)
cold receptors
IV
C (Erlinger-Gasser)
nociceptors (dull pain)
warmth receptors
SPINAL CORD
autonomic fibers
preganglionic fiber
B (Erlanger-Gasser)
posganglionic fiber
C (Erlanger-Gasser)
(pre is faster than post)
GRAY MATTER
rexed laminae
dorsal horn
I - VI
intermediate zone
VII
ventral horn
VIII - IX
GRAY MATTER
dorsal horn
(general statements)
sensory stimulation
(fibers enter the dorsolateral part of spina, via dorsal root)
+
neurons project to higher levels in CNS
+
part of neurons participate in reflexes
GRAY MATTER
dorsal horn
(rexed laminae)
medial division
proprioception (Ia and Ib, A-alpha fibers)
touch (II, A-beta fibers)
lateral division
sharp pain + cold (III, A-delta fibers)
dull pain, warmth (IV, C fiber)

GRAY MATTER
ventral horn
(general statements)
innervation of skeletal muscle
alpha + gamma motoneurons
dorsal fibers - flexors
ventral fibers - extensors
medial fibers - proximal musculature
lateral fibers - distal musculature

GRAY MATTER
ventral horn
(alpha and gamma motoneurons)
alpha motoneurons
A-alpha (Erlanger-Grasser)
extrafusal fibers
neuromuscular junction
gamma motoneurons
A-gamm (Erlanger-Grasser)
intrafusal fibers
muscle spindle (make more sensible to stretch)
GRAY MATTER
intermediate zone
T1 - L2
contains preganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies
+
Clarke nucleus (unconscious proprioception to the cerebellum)
NEURAL SYSTEMS
concept
systems in spinal cords use neurons in the gray matter and tracts or fasciculi of white matter
3 major (motor, sensory and autonomic)
can be found in all levels of CNS
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(basic neural circuit)
voluntary contraction
basic neural circuit: two motoneurons
upper + lower
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(lower motoneuron)
ventral horn (spinal cord) - fibers exit in ventral root
and
cranial nerve nuclei - fibers exit in cranial nerve
synapse directly in neuromuscular junction
(motor unit)
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(upper motoneuron)
cell bodies in brain stem and cerebral cortex
axons descend via tract (spinal cord)
synapse with lower motoneuron or interneurons
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(upper motoneuron)
cell bodies
red nucleus
reticular formation
lateral vestibular nuclei
cerebral cortex (most important)
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(upper motoneuron)
pathway
note: UMNs have net inhibitory effect on muscle stretch reflexes

MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(corticospinal tract)
fibers distribution
60% of the fibers
precentral gyrus - primary motor cortex and premotor area (Brodmann 4 and 6)
40% of the fibers
somatosensory cortical areas (parietal lobe)
MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(corticospinal tract)
pathway
cerebral cortex
internal capsule
brain stem (ventral portion)
decussation of the pyramids (80-90%)
lateral corticospinal tract (contralateral in spinal cord)
ventral horn to synapses

MOTOR SYSTEM
voluntary innervation of skeletal muscle
(corticospinal tract)
clinical correlate
Lesions above pyramidal decussation
contralateral weakness
Lesions below this level
ipsilateral weakness
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(reflex)
sensory stimulus
(Ia, Ib afferents or pain fibers)
→
synapse in spinal cord
(mono or polysynapses)
→
lower motoneuron response
(contration or relaxation)
both alpha and gamma
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(flexor withdrawal reflex)
protective reflex
painful stimulus → spinal cord → withdrawal of stimulated limb
crossed extension reflex (to support the body)
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(myotatic reflex)
deep tendon reflex
(monosynaptic and ipsilateral)
in response to stretch
(spindles - Ia fibers)
basic mechanism for regulating muscle tone
(alpha motoneurons)
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(common myotatic reflexes)
5

MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(inverse muscle stretch reflex)
collagenous tendon fibers
(golgi tendon organs - Ib fibers)
polysynaptic
(inhibition interneuron)
facilitate antagonists and inhibit agonist
“stretch can be a risc”
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(inverse muscle stretch reflex)
mechanism
golgi tendon organs (Ib fibers)
→
spinal cord - inhibition interneuron
→
direct inhibition action on alpha motoneurons
+
gamma motoneurons and upper motoneurons
(regulation of spindles sensitivity and making the alpha motoneurons increase in muscle tone)
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(stretch reflex vs inverse reflex)
spindles - in parallel with extrafusal fibers
golgi tendon organs - in series with extrafusal fibers

MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(upper motor neuron function)
descending control over the reflexes
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(upper motoneurons lesions)
hyperactive muscle streth reflexes + oversensitive golgi tendon organs
(increase of muscle tone)
=
SPASTIC PARESIS
(ipsilateral - lesion in spinal cord)
(contralateral - lesion above the pyramidal decussation)
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(lower motoneurons lesions)
hyporactive muscle streth reflexes + golgi tendon organs
(reduction of muscle tone)
=
FLACCID PARALYSIS
(initially - muscles fasciculations + fibrilations)
(after - hypotonia + atrophy)
ipsilateral
MOTOR SYSTEM
reflex innervation of skeletal muscle
(lower vs upper motoneurons lesions)

SENSORY SYSTEM
Two ascending pathways with …

DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMNISCAL
+
ANTEROLATERAL (SPINOTHALAMIC)

SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(function)
5
Conscious proprioceptions
Fine touch
Vibration
Pressure
Two-point discrimination
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(receptor)
PMM
Pacinian corpuscle
(vibration)
Meissner corpuscle
(touch)
Muscle spindle
(proprioception)
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(primary afferent neurons)
Cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia
Enter the cord via class II or A-beta dorsal root fibers
fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus
(dorsal funiculus)
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(fasciculus gracilis vs fasciculus cuneatus)
GRACILIS
all spinal cord levels
medial
lower extremities/trunk
CUNEATUS
only upper thoracic and cervical levels
lateral
upper extremities/trunk
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(secondary afferent neuron)
nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus
(lower part of the medulla - “bulbo”)
cross the midline
(internal arcuate fibers)
ascending in medial lemniscus
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(thirdary afferent neuron)
Ventral Posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus
(VPL)
Thalamocortical fibers project to the primary somesthesic area (somatosensory)
Parietal lobe - postcentral gyrus
SENSORY SYSTEM
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
(lesions)
Astereognosis
Negative vibratory testing (128Hz tuning fork)
Romberg
Ipsi or contralateral

SENSORY SYSTEM
Anterolateral or spinothalamic tract
(function)
3
PAIN
TEMPERATURE
CRUDE TOUCH
SENSORY SYSTEM
Anterolateral or spinothalamic tract
(primary afferent neuron)
Cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia
Enter the spinal cord via class III or A-delta + class IV
Fibers ascend or descend a couple segments in the dorsolateral tract of Lissauer
SENSORY SYSTEM
Anterolateral or spinothalamic tract
(secondary afferent neuron)
Cell bodies in the dorsal horn gray matter
Fibers cross in the white commissure
Spinothalamic tract
SENSORY SYSTEM
Anterolateral or spinothalamic tract
(thirdary afferent neuron)
Ventral Posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus
(VPL)
Thalamocortical fibers project to the primary somesthesic area (somatosensory)
Parietal lobe - postcentral gyrus
SENSORY SYSTEM
Anterolateral or spinothalamic tract
(lesions)
CONTRALATERAL LOSS OF PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
(unilateral lesions)
information crosses almost as soon as it enters
anesthesia - 1 to 2 segments below the lesion + everything below that level
(Lissauer’s tract)

SENSORY SYSTEM
Spinocerebellar pathways
(two major pathways)
DORSAL SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACT
(lower extremities and trunk)
CUNEOCEREBELLAR TRACT
(upper extremities and trunk)
SENSORY SYSTEM
Spinocerebellar pathways
(function)
Unconscious Proprioceptive
(muscle spindles + golgi tendon organ)
monitor + modulate moviments
SENSORY SYSTEM
Spinocerebellar pathways
(primary afferent neuron)
Cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia
receptor - muscle spindle and goldi tendon organ
SENSORY SYSTEM
Spinocerebellar pathways
(secondary afferent neuron)
Cell bodies
- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract - Clarke’s nucleus (T1 - L2)
- Cuneocerebellar tract - external cuneate nucleus (medulla - bulbo)
SENSORY SYSTEM
Spinocerebellar pathways
(lesions)
uncommon
hereditary diseases
(Friedreich ataxia - autossomal recessive)
ataxia of gait (initial symptom)
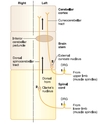
SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Identify cord section
(three tips)
Large Ventral Horn
Both dorsal columns (gracilis + cuneatus)
Lateral Horn

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Identify cord section
(large ventral horn)
YES
C5 - T1 or L2-S2
NO
C1 - C4 or T2 - L1

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Identify cord section
(both dorsal columns)
YES
above T5
NO
below T5

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Identify cord section
(lateral horn)
YES
T1 - L2
NO
C1 - C8 or L3 - S5

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Brown-Séquard syndrome
hemisection of the cord
3 main neural systems
(corticospinal + dorsal columns + spinothalamic)
2 ipsilateral + 1 contralateral (spinothalamic)

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Poliomyelitis
lower motoneurons in ventral horn
→
flaccid paralysis
some patiens recover most function, but others progress to muscle atrophy and permanent disability

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
pure motor system disease
(upper and lower motorneurons)
bilateral flaccid weakness - upper limbs
+
bilateral spastic weakness - lower limbs

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Occlusion of the anterior spinal artery
interrupts blood supply to ventrolateral part of spinal cord
→
corticospinal tract
+
spinothalamic tract
bilateral loss of pain and temperature and spastic paresis

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Syringomyelia
cavitation of the central canal
(cervical spinal cord)
early - white comissure (spinothalamic tract - “belt-like”)
lesion expands - lower motoneurons (ventral horn)
late - Horner syndrome (T1 - T4)
May be present in hydrocephalus and Arnold-Chiari I

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Tabes Dorsalis
Neurosyphilis
Bilateral degeneration of dorsal roots
+
secondary degeneration of dorsal columns
high-step stride and Argyll Robertson pupils

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Subacute Combined Degeneration
patchy losses of myelin in the dorsal columns and lateral corticospinal tracts

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Bladder vs level of the lesion
Above sacral level
spastic bladder
(problems in filing stage - destrusor muscle responds to a minimum amount of stretch)
Sacral level
atonic bladder
(loss of pelvic splanchnic motor innervation - continuous dribble of urine)

SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Brown-Séquard Syndrome - Cervical level



