Specials & NM & RadBio Flashcards
What is the suffix associated with the following types of Gd-based contrast media?
- Linear, ionic compounds
- Linear, non-ionic compounds
Linear, ionic: end in “-ate”
Linear, non-ionic: end in “-mide”
What is the suffix associated with the following types of Gd-based contrast media?
- Macrocyclic, ionic compounds
- Macrocyclic, non-ionic compounds
Macrocyclic, ionic: Gadoterate (only one)
Macrocyclic, non-ionic: end in “-ol”
Which Gd-based contrast agents are good for hepatobiliary imaging?
Ben and Xena Gadobenate + gadoxetate
Which Gd-based contrast agent is good for cardiovascular imaging?
Gadofosveset
What is the suffix associated with the following types of iodine-based contrast media?
- Monomeric, ionic compounds
- Monomeric, non-ionic compounds
Monomeric, ionic: ends in “-ate”
Monomeric, non-ionic: Iohexol, Iopamidol, Iopramide, Metrizamide (Hex Pam’s Pram, ZAM!)

What is the suffix associated with the following types of iodine-based contrast media?
- Dimeric, ionic compounds
- Dimeric, non-ionic compounds
Dimeric, ionic: Hexabrix
Dimeric, non-ionic: trollops + dix (Iotrolan, iodixanol)
What is the particle ratio for each of the following iodine-based contrast media?
- Monomeric, ionic compounds
- Monomeric, non-ionic compounds
- Dimeric, ionic compounds
- Dimeric, non-ionic compounds
- Monomeric, ionic compounds –> 3:2 - Monomeric, non-ionic compounds –> 3:1 - Dimeric, ionic compounds –> 3:1 - Dimeric, non-ionic compounds –> 6:1
Swallow Studies: What is the normal time measured from the onset of swallowing (closure of epiglottis) for each of these factors?
- Opening of the UES
- Max pharyngeal contraction
- Closing of the UES
- Re-opening of the epiglottis
- Opening of the UES: 0.1 sec - Max pharyngeal contraction: 0.15 sec - Closing of the UES: 0.3 sec - Re-opening of the epiglottis: 0.3 sec
Which cranial nerves contribute to the oropharyngeal phase of swallowing?
CN 5, 7, 9, 10, 12
What is the effect of positioning a patient in lateral recumbency on your swallow study?
Increases transit time in the cervical esophagus, fewer primary peristaltic waves.
Which cranial nerve(s) contribute to the cricopharyngeal phase of swallowing?
CN 10 and 12
Which cranial nerve(s) contribute to the esophageal phase of swallowing?
CN 10
What is the normal pharyngeal constriction ratio in the dog? How is it calculated?
0.15 +/- 0.3 PCR = #pixels in max constriction frame / #pixels in hold frame
How might you distinguish pharyngeal weakness from cricopharyngeal dyssynchrony?
PCR will be similar (~ 0.6) but the time to UES opening will be different.
Weakness will have normal time to opening (~0.1 sec) and dyssynchrony will be delayed (~0.3 sec)
What is responsible for the difference in appearance of these two studies?
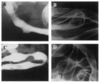
The addition of carboxymethylcellulose – leads to thinner, more uniform mucosal coating
Risks of barium aspiration vs. iodinated contrast aspiration?
Barium – pneumonia, granuloma formation; but mostly will be phagocytosed and transported to TB LN
Iodinated contrast – severe, potentially fatal pulmonary edema
What are the normal GI transit times for the bearded dragon?
- Gastric emptying time
- Small intestinal arrival and emptying time
- Cecum arrival time
- Time to reach the colon
- Gastric emptying time: 10 h (range 4–24 h)
- Small intestinal arrival time: 1 hour
- Small intestinal emptying time: 29 hours
- Cecum arrival time: 10 hours
- Contrast in the colon: 31 hours
(image obtained at 12 hours)

What is the dose for positive contrast gastrography in dogs?
Barium 20-30% w/v
Small dog: 8-12 ml/kg
Large dog: 5-7 ml/kg
What is the dose for pneumocolonogram?
1-3 ml air/kg BW
What are the radiographic measurement parameters for megacolon in cats?
Ratio –> max colonic diameter/length of L5
Normal: <1.3 (1.28)
Megacolon: >1.5 (1.48)
In what recumbency do you perform negative or double contrast cystography/cystourethography? Why?
Left lateral recumbency; if air embolization occurs, it is trapped in the right heart until it is (hopefully) absorbed.
What is the recommended dose and concentration of contrast for shoulder arthrography in the dog?
Dose: 1.5 - 4 ml, diluted to about 100 mg/ml
What are some common abnormal findings related to the biceps tendon in canine shoulder arthrography?
- Absent or incomplete filling of the biceps tendon sheath
- Synovial proliferation
- Inflammation
- Adhesions between tendon and sheath
- Joint mice
- Irreguarity of the tendon sheath margins
- Widening of the distal aspect of the tendon sheath
What are the indications for a right ventricular angriogram?
- Pulmonic stenosis
- Right to left shunt (TOF, reverse PDA, VSD)
- Left to right VSD (will see simultaneous filling of left and right ventricles once contrast gets to the left side of the heart, NOT before)
- Eisenmenger syndrome
What are the indications for left ventricular angiogram?
- Mitral insufficiency
- Subaortic stenosis
- VSD
What are the indications for an aortic injection angiogram?
- Aortic insufficiency
- PDA
- Reverse PDA
- Coronary artery studies
NM QUALITY CONTROL:
What is the cause of each of these images? What is this appearance called?

LEFT: PHA window setting above photopeak
RIGHT: PHA window setting below photopeak
Off peak flood image – shows poor uniformity

What is the typical resolution of a gamma camera? Given this resolution, what is the largest pixel size possible?
Typical camera has resolution: 4.5 mm FWHM
Pixel size cannot exceed 1/3 FWHM of camera –> pixel < 1.5mm
What is the relationship between matrix size and count density?
The smaller the matrix size, the higher the count density
What type of collimator would you choose for imaging each of the following radionuclides?
- 99mTc
- 67Ga
- 111In
- 201TI
- 18F
- 123I
- 131I
- Low energy: 99mTc, 201TI, 123I
- Medium energy: 111In, 131I
- High energy: 18F, 67Ga
What are the characteristics of a high-resolution collimator? What is the trade-off in terms of sensitivity?
High resolution collimators have thick and tall septae with small holes. Higher resolution means a tradeoff with count rate (lower sensitivity)
What are the relative advantages and disadvantages of converging and diverging collimators?
Converging: increased spatial resolution
Diverging: increased FOV
What is the schedule for quality control? Which task(s) should be performed daily vs. weekly vs. bi-annually?
Daily: Peaking PHA, visual inspection of field uniformity, extrinsic quantitative assessment of uniformity
Weekly: visual inspection of field uniformity, extrinsic AND intrinsic quantitative assessment of uniformity, linearity and spatial resolution, sensitivity
Bi-annually: off-peak flood images
What are some of the factors that DECREASE spatial resolution? (8)
- Thicker scintillation (NaI) crystals
- Increased collimator-to-patient distance
- Larger % of photons are allowed to pass through the collimator –> increased scatter
- Increased collimator hole diameter
- Decreased collimator hole height
- Low count density
- Larger PMT
- Incorrect PHA setting
- If centered below photopeak, the recorded image is created primarily from scatter radiation and NOT primary photons
- Patient movement
What are some parameters you can change to increased count density? (5)
- Increase acquisition time
- Smaller matrix
- Larger dose of radiopharmaceutical
- Use a general purpose, low-energy collimator (LEAP)
- Image filters (smooth or Metz filter)
What is the latency period for leukemia? Solid tumors?
Leukemia: 5-7 years
Solid tumors: up to 60 years
Reproductive effects of radiation:
- Doses for oligospermia, azoospermia, and permanent sterility?
- Dose for permanent sterility in the female? What factor does this depend on?
- Male
- Oligospermia: 0.15 Gy
- Azoospermia: 0.5 Gy
- Permanent sterility: 6 Gy
- Female: dose required for permanent sterility is age-dependent and decreases over time
- 12 Gy (prepubertal) to 2 Gy (premenopausal)
What is the doubling dose?
What is the hereditary risk for
- Doubling dose (relative mutation risk ): the amount of radiation required to produce as many mutations as occur spontaneously in a generation.
- Hereditary risk of radiation depends on the population
- General: 0.2 %/Sv
- Working: 0.1 %/Sv
- What is the minimum dose required in a single fraction to induce cataractogenesis?
- What is the latent time for this dose?
- What is the minimum dose required in a single fraction to induce cataractogenesis? 0.5 Gy
- Used to be 2 Gy… 0.5 is the new standard
- What is the latent time for this dose? 8 years
What is the difference between a deterministic and a stochastic effect?
- Deterministic: will definitely occur when a threshold dose is met (e.g. cataracts)
- Stochastic: no threshold dose; these can happen at any dose, however the probability of an effect will increase with increasing dose (e.g., cancer)
NCRP Guidelines for Radiation Exposure:
- Occupational exposure
- Lifetime effective dose
- Annual effective dose
- Pregnancy
- Non-occupational exposure
- Annual effective dose equivalent for continuous/repeated exposure and infrequent exposure
NCRP Guidelines for Radiation Exposure:
- Occupational exposure
- Lifetime effective dose: age in years x 10mSv
- Annual effective dose: 50 mSv
- Pregnancy: 0.5 mSv/month
- Non-occupational exposure
- Annual effective dose equivalent for continuous/repeated exposure and infrequent exposure
- Continuous: 1 mSv
- Infrequent: 5 mSv
- Annual effective dose equivalent for continuous/repeated exposure and infrequent exposure
NCRP Guidelines for Radiation Exposure:
- Occupational exposure – annual limits
- Lens of the eye
- Skin/hands/feet
- Non-occupational exposure – annual limits
- Lens of the eye
- Skin/hands/feet
- Occupational exposure – annual limits
- Lens of the eye: 50 mGy
- Skin/hands/feet: 500 mSv
- Non-occupational exposure – annual limits
- Lens of the eye: 15 mSv
- Skin/hands/feet: 50mSv
When are dosimeters required?
Whenever the worker is likely to receive more than 10% of the annual occupational dose limit (i.e. 10% of 50 mSv = 5 mSv)
There are three whole-body radiation syndromes:
- What are they?
- At what dose do they occur?
- What is the course of disease?
- Hematopoietic syndrome
- Occurs at doses of 2.5-5 Gy
- Peak incidence of death at 30-60 days post-exposure
- Nausea/vomiting followed by symptom-free latent period
- Death due to sepsis
- GI syndrome
- Occurs at doses >10 Gy
- Death 3-10 days later and 100% assured
- CNS syndrome
- Occurs at doses >100 Gy
- Death within hours
Ionization chamber
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- Can they measure exposure rates?
Proportional counter
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- Can they measure exposure rates?
Geiger-Muller counters
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- Can they measure exposure rates?
Ionization chamber
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- alpha, beta, gamma and can be differentiated
- Can they measure exposure rates? Yes
Proportional counter
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- alpha, beta, and can be differentiated
- Can they measure exposure rates? No?
Geiger-Muller counters
- What types of radiation can be detected?
- x-ray, gamma, alpha, betaCANNOT be differentiated
- Can they measure exposure rates? technically but very crude measurement


