Pathophysiology Flashcards
(37 cards)
Gastrin (production site, action, and release stimulus)
Source: G cells
Action: Stimulates acid secretion and growth of stomach epithelium, increases SI and LI peristalsis
Stimulus: Food, partially digested proteins, increased pH of stomach
Cholecystokinin (production site, action, and release stimulus)
Source: I cells
Action: Increases pancreatic enzyme release, inhibits HCl production in stomach, decreases gastric emptying, potentiates secretin
Stimulus: Fatty chyme, partially digested proteins
Secretin (production site, action, and release stimulus)
Source: S cells in the SI
Action: Inhibits gastric secretions and motility, increases pancreatic enzyme release, increases bile output
Stimulus: acidic chyme, fatty acids, proteins
Somatostatin (production site, action, and release stimulus)
Source: Duodenal and gastric mucosa
Action: Inhibits gastric and pancreatic secretions, inhibits contraction of gallbladder, inhibits intestinal absorption
Stimulus: Food in stomach, sympathetic stimulation
Motilin (production site, action, and release stimulus)
Source: Duodenal mucosa
Action: Stimulates MMC
Stimulus: Fasting
Acid secretion in the stomach is stimulated by….
Acetylcholine, gastrin, histamine
UPPER GI STUDIES (DOGS, LIQUID BARIUM):
- Time for contrast to reach duodenum
- Gastric emptying time
- SI transit time (when it reaches cecum or colon)
- SI emptying time
- Time for contrast to reach duodenum: 15-25 minutes
- Gastric emptying time: 30-120 minutes
- SI transit time (when it reaches cecum or colon): 30-120 minutes
- SI emptying time: 3-5 hours
(approximately similar between Wallack, 2003 and O’Brien, 1973)
UPPER GI STUDIES (CATS, LIQUID BARIUM):
- Time for contrast to reach duodenum
- Gastric emptying time
- SI transit time (when it reaches cecum or colon)
- Time for contrast to reach duodenum: 10 min
- Gastric emptying time: 15-60 min
- SI transit time (when it reaches cecum or colon): 30-60 min
- SI emptying time:
Source: Morgan, 1981
UPPER GI STUDIES (FOALS, LIQUID BARIUM)
- Gastric emptying time
- Barium filling cecum
- Transit time to transvers colon
- Gastric emptying time: Variable, but almost all gone within 2 hours
- Barium filling cecum: 2 hours
- Transit time to transvers colon: 3-8 hours (slower with increasing age)
Source: Campbell, 1984
Name the numbered structures in this image

- Nasopharynx
- Soft palate
- Base of tongue
- Epiglottis
- Trachea
- Cranial esophageal sphincter
- Cranial esophagus with barium in the lumen

What is cricopharyngeal achalasia?
Failure of the UES to open fully or open at the appropriate time
What is the progression of distension of the components of the biliary system in EHBDO?
Day 1: GB and cystic duct dilated
Day 1-2: CBD dilated
Day 5-7: distension of intra-hepatic ducts
What is GFR (definition)?
What is normal in dogs?
What is normal in cats?
GFR = the quantity of filtrate formed in the kidney/minute
Dogs: >3 ml/min/kg
Cats: > 2.5 ml/min/kg
What range of GFR likely indicates subclinial renal insufficiency?
1.2 - 2.5 ml/min./kg
What is the resistive index measuring in the kidney?
What is considered the cutoff for an abnormal kidney in a dog?
RI = (systolic velocity - diastolic velocity) / systolic velocity
Measure of vascular resistance within the kidney
RI > 0.7 is abnormal
What is the effect of each of the following hormones on the Ca:P ratio?
1) Calcitonin
2) PTH
3) Calcitriol
- Calcitonin: decrease Ca, minimal effect on P
- PTH: increase Ca, decrease P
- Calctriol: increase both
Explain the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). What stimulates RAAS?
- Decreased BP in the afferent arteriole
- Increased sympathetic tone
- Decreased Na & Cl concentration at the macula densa (low GFR leads to over re-absorption in the ascending LOH)
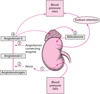
What is the effect of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)? What stimulates secretion of ANP?
Dilation of afferent arteriole –> increased GFR
Decreases renin production –> natriuresis & diuresis
Stimulated by atrial distension
RADIOGRAPHIC FETAL OSSIFICATION INTERVALS
(Days Post-LH Peak)
- Mineralization of bones
- Radius/Ulna/Tibia
- Pelvis
- Distal extremities and teeth
- Also, what is gestation time in a dog?
(Days Post-LH Peak)

- Mineralization of bones: 45 days
- Radius/Ulna/Tibia: 52 days
- Pelvis and ribs: 54 days
- Distal extremities and teeth: 61 days
- Also, what is gestation time in a dog? About 64 days
Fetal mineralization in cats on radiographs
Same sequence of mineralization as dogs, but everything except mineralization of the teeth happens a few days earlier.
What are the radiographic signs of fetal death? (6 things)
- Gas within the uterus
- Lack of mineralization of the fetus at an appropriate time
- Demineralization of fetal skeleton
- Abnormal fetal position (rolling into a ball)
- Overlap of the skull bones (Spalding sign)
- Increased opacity of fetus with decreased visualization of the extremities
Timing of pyometra: what part of estrus cycle
1-3 months post-estrus in the diestrus phase
What are considered normal measurements of the prostate on radiographs?
Lateral view: < 70% of the height of the pubic-sacral promontory
VD view: <50% of the pelvic inlet width

Differential diagnoses for diffusely decreased bone density (osteopenia)
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Hyperparathyroidism (nutritional, renal, primary)
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Glucocorticoid excess
- Osteoporosis
HOG MOV(e)







