Skin structure and function 3 Flashcards
(32 cards)
What is the dermo-epidermal junction ?
Interface between epidermis and dermis

What is the function of the dermo-epidermal junction?
•Key role in epithelial–mesenchymal interactions:
- –Support, anchorage, adhesion, growth and differentiation of basal cells
- –Semi-permeable membrane acting as barrier and filter
Note mesenchymal = Mesenchymal cells are able to develop into the tissues of the lymphatic and circulatory systems, as well as connective tissues throughout the body, such as bone and cartilage.
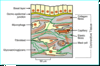
Appreciate the structure of the dermo-epidermal junction as shown in the pic

- Basal cells
- Lamina lucida
- Lamina densa
- Sub-lamina densa zone
Think Big Ladies Dont Sprint
What condition is shown here ? (describe the condition briefly)

Bullous phemphigoid:
Bullous pemphigoid is an acute or chronic autoimmune skin disease, involving the formation of blisters, more appropriately known as bullae, at the space between the skin layers epidermis and dermis. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction, with the formation of anti-hemidesmosome antibodies.
If bullous phemphigoid is suspected what is done to confirm the diagnosis ?
A skin biopsy is taken to confirm it, immunofluroescence may be used to show up the antibodies, and a blood sample may be taken and checked for the presence of pemphigoid antibodies.

Name and briefly describe the condition shown here ?
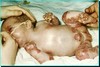
Epidermolysis bullosa - Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of inherited connective tissue diseases that cause blisters in the skin and mucosal membranes, with an incidence of 20 per million newborns in the United States. It is a result of a defect in anchoring between the epidermis and dermis, resulting in friction and skin fragility.
What is the dermis made up of ?
It is made up of:
- Ground substance - The ‘ground substance’ of extracellular matrix is an amorphous gelatinous material. It is transparent, colourless, and fills the spaces between fibres and cells. It actually consists of large molecules called glycosoaminoglycans (GAGs) which link together to form even larger molecules called proteoglycans.
- Cells - mainly fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, lymphocytes and Langerhans cells
- Muscles, blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves
The person on the left is actually the older of the two, why might the person on the right appear older ?

Photoaging - Photoaging is premature aging of the skin caused by repeated exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV) primarily from the sun, but also from artificial UV sources.
Describe the flow of blood in skin
Arteriole ====> precapillary sphincters =====> arterial =====> venous capillaries ====> post-capillary venules =====> collecting venules

What is shown here and briefly describe what it is

Angioma - A tumor (abnormal growth), such as a hemangioma or lymphangioma, that mainly consists of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels.
Describe the lymphatic vessels in the skin
Subepidermal meshed networks.

Smaller non-contractile vessels ====> larger contractile lymphatic trunks
What do lymphatic vessels do and what are there important immune functions ?
- Continual drainage of plasma proteins, extravasated cells and excess interstitial fluid
- Important immune functions:
- immune surveillance by circulating lymphocytes and Langerhans cells
- channelling of micro-organisms / toxins
Name and briefly describe the condition shown here ?

Chronic lymphoedema:
Lymphedema is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system
What are the specialised somatic sensory receptors found in the skin ?
Pacinian corpuscles and Meissners corpuscles and free nerve endings

What do Pacinian corpuscle receptors sense in the skin ?
Pressure
What do Meissners corpuscles sense in the skin ?
Vibrations
What are the areas that somatic sensory innervation is arranged into called ?
Arranged into dermoatomes
Describe the innervation of the skin
The entire surface of your skin receives its nerve supply from the central nervous system (CNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Your central nervous system receives sensory information about touch, pressure, temperature and pain from areas of your skin. (these areas = dermatomes).
Receptors in different areas of your skin send nerve impulses or messages via spinal nerves to the spinal cord. This information is then transmitted up the sensory or ascending spinal tracts in your spinal cord to the brain.
The autonomic nervous system controls the blood vessels, sweat glands and oil (sebaceous) glands in your skin.
What does the autonomic nerve supply control in the skin ?
Blood vessels, nerves and glands
What is shown here ?

Pacinian corpuscles
Name and briefly describe the condition shown ?
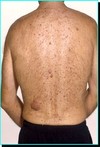
Neurofibromatosis:
- Neurofibromatosis is the general name for a number of genetic conditions that cause tumours to grow along your nerves.
- Tumours are swellings formed by a growth of cells. In neurofibromatosis, the tumours are usually non-cancerous (benign).
What are the 3 main different skin glands in the skin ?
- Sebaceous
- Apocrine
- Eccrine
Label the skin glands as indicated by the arrows


How do sebaceous glands secrete and what do they secrete ?
- Holocrine secretion into pilary canal
- Secrete sebum - which is a oily, waxy substance made up of squalene, wax esters, TG (triglycerides) and FFA (free fatty acids)
Note - Holocrine secretions are produced in the cytoplasm of the cell and released by the rupture of the plasma membrane.
Also these glands are inactive pre-puberty and are the biggest on the chest and face








