Skin examinations - (clinical skills related) Flashcards
What should your approach be when carrying out a skin examination ?
Should be methodical assess and record in turn:
- Distribution - which areas are affected
- Configuration- how lesions are arranged – helps with pattern recognition
- Morphology - what the lesion(s) look like – consider magnifying lens – Palpate (feel) as well as look
Examining what other areas might give you an idea of what is the underlying skin conditions ?
- Nails : e.g. In psoriasis: pitting (depressions of nail plate) and onycholyisis (separation of nail plate from bed) are common findings
- Mouth : e.g. blistering disease – may see erosions of buccal mucosa
- Joints :e.g. psoriasis: look for signs of arthritis
- Hair : changes may be associated with underlying systemic disease – Hypertrichosis – general excess growth – Hirsutes – excess growth in male pattern (e.g. beard area) in women – Alopecia – loss of hair
What should you think about when examining a skin lesion ?
Pick a typical area and assess in turn:
- Colour
- Size
- Raised or flat
- Border features
- Surface features: scale, crust
Describe the type of skin lesion shown here

It is a purpura - also called blood spots or skin hemorrhages, refers to purple-colored spots. This will not blanche
Describe the skin lesion shown here

Petechia - a small red or purple spot caused by bleeding into the skin
(Petechia – smaller 1- 2 mm area of flat purpura)

What skin reaction is shown here ?

Erythema - superficial reddening of the skin, usually in patches, as a result of injury or irritation causing dilatation of the blood capillaries.
What type of pigmentation change is shown?

Hypopigmentation - It is caused by melanocyte or melanin depletion, or a decrease in the amino acid tyrosine, which is used by melanocytes to make melanin.
What type of pigmentation change is shown here?

Hyperpigmentation - condition in which patches of skin become darker in color than the normal surrounding skin. This darkening occurs when an excess of melanin
Describe what type of skin lesion is shown here

Macule - an area of skin discoloration < 1cm
Described as a patch if >1cm
Describe the skin lesion shown

Papule - a small pimple or swelling on the skin, often forming part of a rash.
localised elevated area < 0.5cm
If >0.5 cm then described as a nodule
Describe the appearance of the skin lesion shown

Plaque - A plaque is a palpable flat lesion usually greater than 1 cm diameter. Most plaquesare elevated, but a plaque can also be a thickened area without being visibly raised above the skin surface.
Describe the skin lesion shown
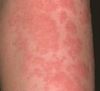
Wheal - A raised, itchy (pruritic) area of skin that is sometimes an overt sign of allergy. Not all wheals are alike. They may be redder or paler than the skin around them. It is a compressible dermal swelling
What type of skin lesion is shown ?

Bulla - A bulla is a fluid-filled sac or lesion that appears when fluid is trapped between the dermis and epidermis
Reffered to as a vescile if < 0.5cm
Bulla if > 0.5cm
Describe the type of skin lesion shown

Cyst - nodule containing semisolid material
Describe the type of skin lesion shown

Pustule - A pustule is a circumscribed elevation of the skin that contains a purulent exudate that may be white, yellow, or greenish-yellow in color. (pus filled)
When describing the border features of a skin lesion/problem what is the main 2 ways it can be defined ?
Can be defined as:
- Well defined/ sharp border (irregular or regular) or
- Poorly defined
How would you describe the border of the skin lesion shown ?

Well defined
How would you define the borders of the skin lesion shown ?

Poorly defined
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Scale - accumulated fragments of keratin layer
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Crust - dried exudate e.g. serum
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Scar - an area of fibrous tissue (fibrosis) that replace normal skin after injury.
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Lichenification - it is a skin condition that occurs in response to excessive itching or rubbing of the skin and results in thick, leathery patches of skin. This occurs because the outer layer of skin naturally thickens with the extra irritation, and it often happens in tandem with eczema or other skin disorders.
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Skin fissure - linear split in epidermis
Describe the type of skin feature shown

Skin atropy - loss of epidermis +/- dermis (surface remains intact)




