Skin Strata ( Identification, Structure, and Function) Flashcards
(36 cards)

Epidermis; five layers (Stratum Basale, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum granulosum, Stratum Lucidum (thick skin), and Stratum Corneum.

Dermis deep to the Epidermis. Contains two layers (superficial papillary layer and the deep reticular layer)

Papillary layer of the dermis ( Superficial to the reticular layer) Represents the upper 1/5th of the dermis, contain collagen, elastic fibers, and areolar connective tissue, dermal papillae, capillary loops, and Meissner’s Corpuscle; immediate to the stratum basale and provides nutrition and oxygen.
What is the purpose for dermal papillae?
Increase SA which helps with contact with the epidermis (strength and sites for nutrition)

Reticular layer, deep to the papillary layer, bottom 4/5th layer, DIRCT, Pacinian Corpuscles,
Merocrine sweat gland (Momo small); Eccrine (simple coiled tubular), contain myoepithelial cells, function: temperature regulation and excretion
(urea, uric acid, ammonia); location (forehead, palms, soles,)

Hair Follicles ( three layers: Cuticle (outer layer keratinized), Cortex ( thick, elongated portion, contains pigment, Medulla (Inner layer, pigment and air).

Sebacceous Glands, produce Sebum, (simple, branched, and acinar), holocrine secretion
Sebum
Fat, cholesterol, and protein mixture produced by the sebacceous glands. Keeps hair from drying (brittle) out and skin, inhibits certain bacteria

Merkel Cells - detect very fine and light touch. Located in the stratum basale of the epidermis.

Arrector Pili Muscle - responsible for contracting and standing hair up, found in papillary layer of the dermis, contract in response to physiological or emotional stress i.e cold or fear, ANS, which traps air for insulation or shows greater/ scarier appearance.

Meissner’s Corpuscle- located in the papillary layer of the dermis, sensitive nerve endings that detect fine touch, pressure, and slow vibrations

Ruffini Corpuscle - located in the dermis, ligaments, and tendons, responsible for crude touch and stretching
Apocrine Sweat gland (Simple, coiled, tubular, exocytosis) ( Appa “bigger sweat glands); need to say apocrine sudoiferous gland, location: axilla, pubic, and anal areas. Activated at puberty responsible for smell, not active during thermoregulatory sweating, secrete pheromones, sweat, in response to emotional stress and sexual excitement, have myoepithelial cells,

Merocrine Sweat glands (Eccrine) - thermoregulation and excretion
Polymastia
mammary glands are specialized apocrine glands

Apocrine Sweat Glands

Pacinian Corpuscle - deep pressure and fast vibrations located deep in the dermis or hypodermis

Hair Follicles.
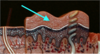
Stratum Corneum - top layer, dead, keratinization complete, lack nuclei,
How long does Keratinization take place and what enzyme is necessary for Stratum Basale to Stratum Corneum stratification?
4-6 weeks, Epidermal growth factor

Stratum Lucidum; Only Present in thick skin (palms and soles); nothing inside of cells except for keratin fibrils and eleidin (Keratin precursor)







