Connective Tissues Flashcards
Types of loose connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue, reticular connective, adipose connective tissue (ARA)
Types of Cartilage
Fibrocartilage, hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage
Types of Dense connective tissue
DRT, DIRCT, ECT
Brown vs. White Adipose Tissue
1) Brown - found mostly in infants , dark, more vascular, higher number of mitochondria 2) white - found mostly in adults, less vascular
Types of connective tissue fibers
1) Collagen fibers 2) Elastic Fibers 3) Reticular fibers
Collagen Fibers
relatively thick, thread-like composed of collagen and occur in long, parallel bundles. can withstand force along long axis
Elastic Fibers
Thinner and form complex networks; branched; return back to normal length after stretch
Reticular Fibers
Highly branched and delicate support networks. Able to resist forces applied from many different directions.
Fixed Cells
Fibroblasts, adipocytes, fixed macrophages, mesenchymal cells, and melanocytes
Wandering Cells
Free macrophages (in blood monocytes), mast cells, lymphocytes, microphages (neutrophils and eosinophils migrate throughout the body and respond to chemicals released by macrophages and mast cells. Also phagocytic)

Simple Squamous Epithelium; Location: Alveoli of the lung, inner lining of the cornea of the eye, mesothelial lining of ventral body cavities, and endothelial lining of the heart and the blood vessels Functions: Filtration, diffusion, secretion, cover (not available in areas of wear and tear)

Simple Squamous epithelium; Location: Alveoli of the lung, inner lining of the cornea of the eye, mesothelial lining of ventral body cavities, and endothelial lining of the heart and the blood vessels Functions: Filtration, diffusion, secretion, cover (not available in areas of wear and tear)

Simple Squamous Epithelium ; Location: Alveoli of the lung, inner lining of the cornea of the eye, mesothelial lining of ventral body cavities, and endothelial lining of the heart and the blood vessels Functions: Filtration, diffusion, secretion, cover (not available in areas of wear and tear)

Stratified Squamous Epithelium Keratiinized; Location: Surface of the skin, lining of the mouth, anus, and vagina Function: Protection against mechanical stress/abrasions/ water loss/ UV radiation/and foreign invasion

Stratified Squamous Epithelium ; Location: Surface of the skin, lining of the mouth, anus, and vagina Function: Protection against mechanical stress/abrasions/ water loss/ UV radiation/and foreign invasion

Stratified Squamous Epithelium Keratiinized; Location: Surface of the skin, lining of the mouth, anus, and vagina Function: Protection against mechanical stress/abrasions/ water loss/ UV radiation/and foreign invasion
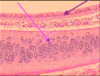
A - Pseudostratified Cilitated Columnar Epithelium B - Hyaline Cartilage ; A Location: trachea, nasopharynx, bronchi of upper respiratory tract Function: cilia move mucus and foreign particles away from site, coughing speeds up the movement of cilia, cilia move oocytes through fallopian tube ; B:Hyaline Cartilage , Type: Cartilage, Location: ends of long bones, anterior ends of ribs, trachea, parts of larynx, Function: provides smooth movements at joints, flexibility and supports, weakest of the three types of cartilage, Presentation: packed collagen fibers not easily seen under the microscope, clear glassy, chondrocytes in lacunae, surrounded by perichondrium, avascular slow to heal

Simple Cuboidal epithelium; Location: portions of the kidney tubules, various glands and ducts Function: secretion of products ( Secretion and absorption)

simple cuboidal epithelium; Location: portions of the kidney tubules, various glands and ducts Function: secretion of products ( Secretion and absorption)

Simple cuboidal epithelium; Location: portions of the kidney tubules, various glands and ducts Function: secretion of products ( Secretion and absorption)

Stratified Cuboidal epithelium; Location: lining ducts of adult sweat glands, esophageal glands, part of male urethra (very rare) Function: (Protection and limited secretion)

stratified cuboidal epithelium ; Location: lining ducts of adult sweat glands, esophageal glands, part of male urethra (very rare) Function: (Protection and limited secretion)

Stratified cuboidal epithelium; Location: lining ducts of adult sweat glands, esophageal glands, part of male urethra (very rare) Function: (Protection and limited secretion)

Transitional Epithelium; Location: Urinary Bladder, renal pelvis, and portions of the ureters and urethra Function: allows urinary organs to stretch to hold variable amounts of fluid without rupturing and serves as a protective lining