SKELETON & JOINTS Flashcards
(23 cards)
Describe the 4 main functions of the skeleton
SPMM
- Support the body
- Protect vital organs
- help the body Move
- Make blood cells
how does the skeleton support the body?

the backbone (spine) keeps the body upright
(or we’d flop over)
how does the skeleton protect the body?
- skull protects the brain
- ribcage protects the heart & lungs
- backbone/spine protects the spinal cord

how does the skeleton move the body?
muscles are attached to bones (your skeleton)
if a muscle pulls on a bone, the bone will move at joints (knee, elbow, ankle)
how does your skeleton make blood cells?
red & white blood cells are made in bone marrow (a soft tissue inside your leg & arm bones)

state the function of red blood cells
carry O2 around the body in the blood

state the function of white blood cells
help destroy harmful infections

where are red & white blood cells made?
in bone marrow
(soft tissue inside larger hard bones)

how many bones do you have?
206
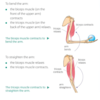
name muscles A and B

A = tricep
B = bicep
What is meant by antagonistic muscles?
a pair of muscles that act on a joint
as one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes

where are joints found?
where 2+ bones join together
name the 3 types of joints in the body
- hinge joints
- ball-and-socket joints
- fixed joints
describe hinge joints
hinge joints allow bones to move

forward & backward
(knee, elbow)
describe ball-and-socket joints
ball-and-socket joints allow bones to move
in all directions
(hip, shoulder)

describe fixed joints
fixed joints do not allow movement
(skull)

what are the ends of bones in a joint covered with to stop them rubbing
cartilage: a strong smooth slippery tissue

what are two bones at a joint held together by?
ligaments

how can you measure muscle strength?
Newton scale

what are muscles made of?
muscle tissue is made from lots
of muscle cells working together

how are muscles attached to bones?
muscles are attached to bones by tendons
can muscles push?
no, muscles can only pull
so muscles work in pairs
(each pulling on the other)
what’s the difference between
a tendon and a ligament?
a tendon is a tissue attaching muscle to bone

a ligament is a tissue attaching bone to bone


