Simple Linear Regression Flashcards
(18 cards)
Assumptions for Simple Linear Regression
Data must be continuous, interval or ratio scale, normally distributed and no significant skewness.
Determining equation of a straight line
Y = a + bX
Least-squares criterion
Regression line is fitted with reference to the difference between the line and individual data points.
Residual
Differences between the data point and the regression line (the unexplained variance)
Variance
Sum of squares/degrees of freedom.
Coefficient of Explanation (r2)
Regression sum of squares of Y/total sum of squares of Y. The proportion of variance that is explained by the model. Regression coefficient or scatter plot indicates positive/negative relationship.
Standard Error
Simply the Squared root of theunexplained variance.
Calculating Confidence/prediction intervals
We can distinguish between confidence intervals around the line itself and the prediction itself and the prediction intervals that describe the estimates to which estimates of Y vary about the line. The prediction intervals are larger and reflect the collective uncertainties of scatter and errors in sampling a and b.
Standardised Residual
Residuals are important because their character has important implications for the regression model. Their magnitude contributes to prediction limits.
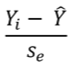
Homoscedasticity
For a model to be wholly reliable, the residuals should be distributed normally about the line. A requirement of homoscedasticity is that the degree of scatter should not vary greatly along the range of X.
Heteroscedastic
For a model to be wholly reliable, the residuals should be distributed normally about the line. If it is not fulfilled the data is said to be heteroscedastic and the regression equation may be unreliable for some purposes.
Autocorrelation
There should be independence between residuals and, consequently, no autocorrelation between them. Autocorrelation is indicated by either long runs of positie or negative residuals along the regression line, or, on the other hand, by rapid and regular fluctuations of residuals.
Measures of autocorrelation
Durbin-Watson d-statistic. Based on the sequence of residuals so that: d = sum of successive squared differences/sum of sqaured residuals.
D-W value - indicate whether to accept or reject null hypothesis. 0.-1.475 indicates positive autocorrelation and 2.5-4.0 indicates negative.
Non-Linear Regression
There are a number of bivariate relationships in Geography in which incremental changes in the predictor variable (X) are not accompanied by correspondingly uniform changes in the dependent variable (Y). Such relationships are said to be linear and are summarised by curves.
Difficulty that lies in non-linear regression
There are many possivle forms of non-linear relationships.
Exponential curves use the universal constant of
2.7182
Partial regression coefficients
Represent changes in slope as X increases and are scale dependent.
Non linear regression power curve
Equation is Y = aXb


