Session 6 - Pelvic Floor Muscles Flashcards



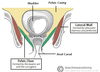
Where do pelvic viscera lie?
Pelvic cavity (true pelvis) found in lesser part of pelvis
What are the 2 holes found in the pelvic floor. What is their function?
- Urogenital hiatus – anteriorly positioned, allows passage of urethra (and vagina in females).
- Rectal hiatus – centrally positioned, allows passage of anal canal.
What is the 3 functions of pelvic floor viscera?
- Support of abdominopelvic viscera through tonic contraction
- Resistance to increase in intra-abdominal pressure during activities such as coughing or lifting.
- Urinary and fecal continence – muscle fibres have a sphincter action on rectum and urethra.
What is the innervation of the levator ani muscles?
Pudendal S2-4
What are the 3 muscles which make up the levator ani?
pubococcygeus, puborectalis, iliococcygeus
What are the 3 components of the pelvic floor?
- Levator ani muscles
- Coccygeus muscle
- Fascia coverings of muscles
What is the function of puborectalis and how does it achieve this?
- Forms sling around rectum
- Maintains faecal continence
What is the perineal body and its function?
Connective tissue mass in centre of perineum
Anchors perineal muscles and rectum
What are the boundaries of the perineum?
Anterior – Pubic symphysis.
Posterior– The tip of the coccyx.
Laterally – Inferior pubic rami and inferior ischial rami, and the sacrotuberous ligament.
Roof – The pelvic floor.
Base – Skin and fascia.
What can the perineum be subdivided into?
Anterior urogenital triangle
Posterior anal triangle
What are the contents of the anal triangle?
Anal aperture
External anal sphincter
2 ischioanal fossae
What are the layers of the urogenital triangle?
- Skin
- Superficial perineal fascia
- Deep perineal fascia
- Superficial perineal pouch
- Perineal membrane
- Deep perineal pouch
What is contained in the deep perineal pouch in males and females?
Both - part of urethra and external urethral sphincter and deep transverse perineal muscles
Males - bulbourethral glands
Females - urethrovaginal sphincter
What is found within the superficial perineal pouch?
Both sexes - ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, superficial transverse perineal muscle. Bartholin’s glands.


What is the neurovascular supply to the perineum?
Pudendal - S2 to S4
Internal pudendal artery
How can damage to the perineal body during labour be avoided?
episiotomy - surgical cut in the perineum which prevents tearing of perineal body
How can damage occur to the pelvic floor during childbirth?
Mechanical - muscles stretched or pudendal nerve damaged.
Iatrogenic - damaged in episiotomy


