Session 4: Carbon Dioxide in the Blood Flashcards
Function of CO2 in blood.
A major role in controlling blood pH and the blood’s acid base balance.
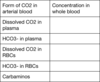
Where can CO2 be found in blood?
In plasma In red blood cells Bound to haemoglobin
How can CO2 be found in plasma?
Dissolved in the plasma
Explain what happens to CO2 when it is dissolved in plasma.
It reacts with water to form H+ and hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate HCO3-)

Why is this reaction slow in plasma?
Because there is little carbonic anhydrase in the plasma.
What does the extent of dissociation of CO2 determine?
The pH of plasma.
What causes the equilibrium to shift towards dissociation?
An increase in dissolved CO2.
What is dissolved CO2 directly proportional to?
Partial pressure of CO2 in the artertial blood
What is normal pCO2 in arterial blood?
5.3 kPa
What is the normal concentration of CO2 in plasma?
(Solubility constant is 0.23 of CO2)
0.23 x 5.3 = 1.2 mmol/dm3
What is dissociation of CO2 resisted by?
High concentrations of bicarbonate HCO3-
What is the normal concentration of bicarbonate in the plasma?
Around 25 mmol/l
Where does the high concentration of HCO3- come from?
Reaction of CO2 in red blood cells.
What is the normal ratio of HCO3- to CO2?
20:1
What does pH depend on?
The ratio of [HCO3-] to pCO2
What happens to pH if pCO2 rises?
pH falls
What happens to pH if HCO3- rises?
pH rises
Explain the Henderson - Hasselbach equation.
pKa = 6.1
Since the normal ratio of HCO3- to CO2 is 20 -> Log20
pH = 6.1 + log20
pH = 6.1 + 1.3
pH = 7.4

Ratio of CO2 to O2 in arterial blood.
2.5:1
What is the total content of CO2 in arterial blood?
Around 21 mmol
Only around 1.2 mmol/l of CO2 can be found in the plasma. Where is the rest of the CO2 found in blood?
In red bloods cells.
How can there be more dissolved CO2 in plasma compared to O2 when pAO2 > pACO2?
Because of the solubility of CO2 in plasma. It is more soluble.
What happens to carbon dioxide in red blood cells?
They can react with water
Can bind to haemoglobin
Explain CO2 in red blood cells reacting with water.
Compared to in the plasma CO2 reacts rapidly with water due to higher concentrations of carbonic anhydrase in RBCs which forms H+ and HCO3-.