Session 10: Radiology II Flashcards
What is important in order to have an adequate image to assess the lungs?
Projection (Usually PA)
Inclusion
Rotation
Lung volumes
Penetration
Inclusion:
What do we need to see on a CXR?
1 st rib
Lateral margin of ribs
Costophrenic angle
Rotation:
What is important to see?
The alignment of the spinous process and clavicles.

Lung volumes:
What is important to see?
A normal lung volume during the inspiratory phase would show 5th to 7th anterior ribs at the midclavicular line.

Why is adequate penetration important?
To make sure the vertebrae are just visible through the heart and so we can see the left hemidiaphragm.

Explain the systemic approach to evaluate a CXR.
Check the patients demographics.
Check that projection, rotation, penetration and lung volumes are alright.
ABCD
Airways
Breathing
Circulation
Diaphragm/Bones
and then lastly review areas.
What is evaluated in adequacy?
RIP
Rotation
Inspiration
Penetration
What is evaluated in airways?
Trachea, bronchi and hila
What is evaluated in breathing?
Lungs
Pleural spaces
Lung interfaces
What is evaluated in circulation?
Mediastinum
Aortic arch
Pulm vessels
Right heart border, right atrium and middle lobe interface
Left hear border, left ventricle and lingula interface.
What is evaluated in diaphragm and bones?
Free gas
Nodules
Fracture/dislocation
Mass
What is evaluated in review areas?
Apices (pneumothorax or malignancy)
Thoracic inlet (mass)
Paratracheal stripe (mass)
AP window (LN)
Hila (mass/collapse)
Behind the heart (mass)
Below diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum/mass)
Bones (fracture/mass/missing bones)
Edge of films


What is the silhouette sign?
Adjacent structures of differing density will form a nice silhouette.
If this silhouette is lost it can locate pathology.

What causes a mediastinal shift (push)?
Increase volume or pressure
What causes a mediastinal shift (pull)?
Decrease voume or pressure
Why might mediastinal shift not be a sign of pathology?
If the image is not adequately centered.
What is this?

Pneumothorax


Pleural effusion
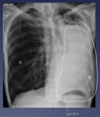
How do pleural effusions show on CXR?
Uniform white area where there is loss of the costophrenic angle and the hemidiaphragm is obscured.
What are the generic findings of a lobar lung collapse?
Elevation of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm.
Crowding of the ipsilateral ribs
Shift of the mediastinum towards the side of the atelectasis.
Crowding of the pulmonary vessels.
What is consolidation?
Filling of small airways/alveoli with something.
What might consolidation be?
Pus (pneumonia)
Blood (haemorrhage)
Fluid (oedema)
Cells (Cancer)
How does consolidation show up on CXR?
Dense opacification
Volume preservation but may be either increased or decreased as well.
Air bronchogram









