session 4 Flashcards
action potential phases
- rapid depolarisation
- plateau
- repolarisation
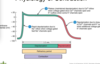
what occurs dueing depol of the heart
fast sodium Na+ channels open for rapid depol
plateau pahse of the heart
- slow calcium channels open
- calcium binds to troponin
- potassium channels open (K+)
repolarisation of the heart
calcium channels close
potassium channels open
This then goes back to resting membrane potential
refractory period
Long Period after a contraction which doesn’t allow a second contraction to occur
- Tetanic contraction therefore not allowed - this is when they just remain contracted
*

electrocardiogram (ECG)
- electrical currents of the heart detected on skin surface
- is a sum of all action potentials of active cells

- A - P-Q segment
- B - QRS complex
- C - S-T segment
- D - P-Q interval
- E - Q-T interval

P wave represents
atrial depolarisation
- impulse from SA node over atria
QRS complex represents
ventricular depol
- spread of impulse through ventricles
T wave represents
ventricular repol
As atrial fibers depolarise the P wave appears. After the P wave begins..
The atria contract
pathway of electrical current
- SA node
- AV node
- slight delay here to let atria contract
- bundle branches
- perkinje fibres
three phases of cardiac cycle
- atrial systole
- 0.1 sec
- atria contract and blood through AV valves into ventricles
- ventricular systole
- 0.3 sec
- ventricles contract and AV valves close
- ventricular ejection
- relaxation period
- 0.4 sec
- ventricular diastole
- ventricular filling
End diastolic volume is
the amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole
define isovolumetric contraction
- AV and SL valaves are all closed
- ventricular volume remains the same
ventricular ejection
- pressure rises and SL valaves open = blood ejection from heart
end systolic volume ESV
amount of blood in the left ventricle at the end of systole
stoke volume
volume ejected per beat from each ventricle
ventricular pressures
- maximum BP in aorta is 120mmHg
- max in pulmonary trunk 30mmHg
why is left ventricular wall thicker
ejects same amount of blood with more force
auscultation
- listening to sounds within body
- can hear heart sounds which result from turbulent blood flow and valve closure
Four heart sounds
- S1 (lubb)
- closing of AV valves
- S2 (dupp)
- closing of SL valves
- S3
- rapid ventricular filling
- S4
- during atrial systole
Can only hear sound 1 and 2 in normal heart

Heart murmur
Abnormal heart sound
- some can be from backward blood movement in the heart
Cardiac output
- volume of blood from ventricle into aorta each minute
- CO = SV x HR
*
what influences stroke volume
- preload
- frank-starling law of the heart
- increased filling = more muscle stretch = more blood pumped out
- contractility
- afterload
- pressure heart has to overcome before semilunar valve can open

regulation of heart rate
- neural factors
- sympathetic impuses increse HR and contraction force
- parasymp decresae HR
- hormones and ions
- eg adrenaline
- other factrs
- eg age, gender

heart disease risk factors
- high cholesterol
- high BP
- smoking
- diabetes
- high fibrinogen levels
clinical heart issues
- MI = myocardial infarction
- death of heart muscle from low oxygen
- replaced with scar tissue
- blood clot
- angina pectoris
- heart pain from ischaemia
coronary artery disease/ coronary heart disease
- heart receives inadewuate blood due to obstruction of its supply
- eg
- atherosclerosis
- coronary artery spasm
- clot
congestive heart failure
- brought on by high BP, MI or CAD
- heart begins to fail
- left ventricular failure = pulmonary oedema
- right ventricular = peripheral oedema


